Question
Question: EDTA has coordination number (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6...
EDTA has coordination number
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 6
Solution
Hint : The total number of atoms, ions, or molecules bound to an atom in a particular molecule or crystal is referred to as the coordination number of that atom. The coordination number of an atom is sometimes referred to as its ligancy. The ligands are the atoms, ions, or molecules that are bound to the centre atom (or molecule/ion). When determining the coordination number of a central atom in a crystal, the ligancy of molecules is computed differently.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The aminopolycarboxylic acid ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) has the formula [CH2N(CH2CO2H)2]2 . This water-soluble white substance is commonly used to bind iron and calcium ions. As a hexadentate ("six-toothed") chelating agent, it binds these ions. EDTA comes in a variety of forms, including disodium EDTA, sodium calcium edetate, and tetrasodium EDTA. EDTA4− belongs to the aminopolycarboxylic acid family of ligands in coordination chemistry. The two amines and four carboxylates in EDTA4− typically bond to a metal cation.
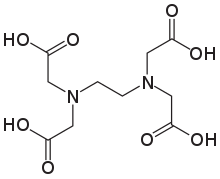
The coordination number for EDTA is 6. The coordinate number of the metal or ion is the number of ligand atoms that are directly attached to the core metal atom or ion by the coordinate bond. It's the number of chemical bonds formed between the ligand and the core metal atom or ion.
Hence option d is correct.
Note :
Concerns regarding the biodegradability of aminopolycarboxylates like EDTA have sparked interest in environmental safety. Alternative aminopolycarboxylates are being investigated as a result of these issues. Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA), iminodisuccinic acid (IDS), polyaspartic acid, S,S-ethylenediamine-N,N′-disuccinic acid (EDDS), methylglycinediacetic acid (MGDA), and L-Glutamic acid N,N-diacetic acid, tetrasodium salt are examples of potential chelating agents (GLDA).
