Question
Question: Eccentric angle of a point on the ellipse \({{\text{x}}^2} + 3{{\text{y}}^2} = 6\) at a distance \(\...
Eccentric angle of a point on the ellipse x2+3y2=6 at a distance 3 units from the centre of the ellipse is
A .35π
B. 3π
C .43π
D .32π
Solution
Hint: Proceed the solution of this question by using general parametric coordinates of any point P on ellipse which is (acosθ, bsinθ) then find the distance between center (which is origin) and point P and equalise it with the given distance in the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the question, given equation of ellipse is x2+3y2=6
On comparing it with standard equation of ellipse which is a2x2+b2y2=1
Equation of given ellipse is x2+3y2=6
Divide by 6 on both side to convert it into standard form
6x2+2y2=1
so on comparing with standard equation of ellipse
a = 6 and b = 2
We know that, the parametric coordinate of any point P on the ellipse is
(x=acosθ and y=bsinθ); Where θ is the eccentric angle.
So the parametric coordinate of point P is (√6cosθ, √2sinθ) (∵a = 6 and b = 2) Here θ be the eccentric angle of the point P.
The center of the ellipse is at the point of origin (0,0)
It is given that 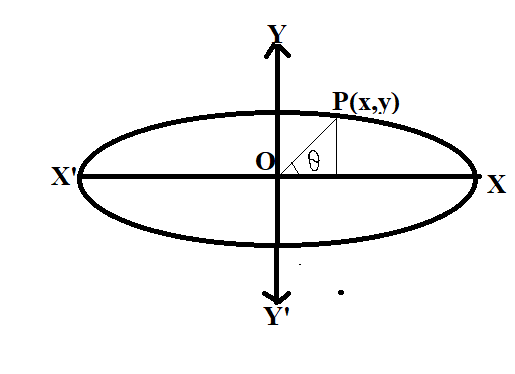
∴OP = 3
So to find length of OP,
Let the coordinates of point O (x1,y1) and P (x2,y2)
So Distance between two points O and P will be = (x2−x1)2+(y2−y1)2
O= (0, 0), P= (√6cosθ, √2sinθ)
Here, x1=0,y1=0,x2=6cosθ,y2=2sinθ
So length of side OP = (6cosθ−0)2+(2sinθ−0)2 = 6cos2θ+2sin2θ
but It is given that OP = 3
so, 6cos2θ+2sin2θ = 3
On squaring both side
⇒6cos2θ+2sin2θ = 3
⇒6(1−sin2θ)+2sin2θ = 3
⇒6−6sin2θ+2sin2θ = 3
⇒6−3=6sin2θ−2sin2θ
⇒43=sin2θ
⇒sinθ=±23
⇒sinθ=+23 or sinθ=−23
⇒θ=sin−1(+23 )or θ=sin−1(−23)
⇒θ=3π,32π or θ=34π,35π
⇒so, eccentric angle θ=43π given in option C
Hence, Option A, B and D all are correct.
Note: In such types of particular questions, where we have assumed Parametric coordinates (trigonometric function of eccentric angles θ). In the solution we got 4 values of θ. This happens because we can assume 4 such values in each quadrant. Therefore, exactly we got 4 such values of θ in each quadrant. These 4 values of θ will also be a mirror image of each other about the x and y axis correspondingly.