Question
Question: During the propagation of a nerve impulse, the action potential results from the movement of: (a) ...
During the propagation of a nerve impulse, the action potential results from the movement of:
(a) K+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
(b) Na+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
(c) K+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
(d) Na+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
Solution
Neural membranes possess various types of ion channels which are selectively permeable to different types of ions. In resting state i.e. when no impulse is being conducted, high concentration of K+ ions is inside the axonal part of the neuron.
Complete answer:
In resting state, the channels on the axonal membrane are more permeable to K+ ions and almost impermeable to Na+ ions. Along with Na+ ions, the axonal membrane is also impermeable to negatively charged proteins. These proteins are present inside of the membrane with a high concentration of K+ ions. This results in a dominance of negatively charged species inside of the cell.
Consequently, the Na+ ions and positively charged proteins are present in high concentration on the outside of the cell i.e. in the extracellular fluid. Hence, a concentration gradient is formed such that the outer membrane has a more positive charge and the inner membrane has a more negative charge. So, in resting-state, we can represent the charges in the intracellular and extracellular fluid as,
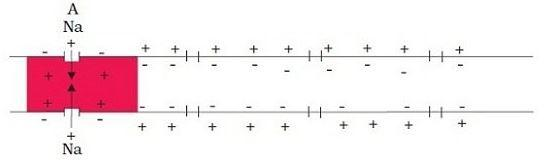
When a stimulus is given to this site, the permeability of the membrane at site A is reversed i.e. it becomes freely permeable to Na+ ions. As a result, Na+ ions enter inside the cell rapidly, and hence the concentration of Na+ increases inside the cell which thus makes the membrane positively charged from inside and negatively charged on outside. This is also referred to as depolarization of site A. The potential difference between the membranes at this point is called an action potential. The current flow further since the site immediately next to A had opposite polarity.
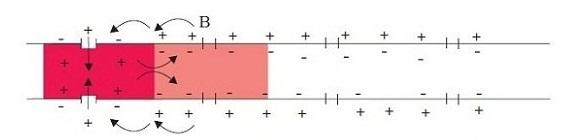
So, the correct answer is Na+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid.
Note: The concentration gradient in the resting-state is always maintained by the constant exchange of ions by the sodium-potassium pump. This pump transports 3 ions of Na+ outside per 2 ions of K+ inside the cell.
