Question
Question: During extraction of aluminium from bauxite: A. the concentration of ore is done by gravity separa...
During extraction of aluminium from bauxite:
A. the concentration of ore is done by gravity separation method
B. molten mixture of aluminium oxide, cryolite or fluorspar is electrolysed
C. impure aluminium is defined by liquation
D. molten aluminium is obtained at cathode while fluorine is liberated at anode.
Solution
The alumina is soluble in a mixture of molten cryolite and fluorspar which lowers the melting point. It is then electrolysed in a square metallic tank with carbon lining, which serves as cathode. Anode consists of thick carbon rods suspended from the top into the fusedAl2O3.
Complete step-by-step solution:
To answer this question, at first, we have to know the process of aluminium extraction from bauxite. Aluminium ore is called bauxite. First step in extraction of aluminium is purification of bauxite ore.
1)The bauxite is made impurity free to provide aluminium oxide from which aluminium can be extracted. The purification process is done with the help of leaching process.
Leaching of alumina from bauxite:
There are many impurities, such as iron oxide, silicon oxide and titanium oxide. The bauxite ore is concentrated by reacting powdered ore with concentrated NaOHat a temperature range of 473-523 K and 35-36 bar pressure. In this way leaching of aluminium in the form of sodium aluminate takes place and impurities are left behind.
Al2O3(s)+2NaOH(aq)+3H2O(l)→2Na[Al(OH)4](aq)
The neutralization of aluminate solution is done by passing carbon dioxide gas which results precipitatation of Al2O3. At this stage, the solution is injected with freshly prepared sample of hydrated Al2O3that causes precipitation.
2Na[Al(OH)4](aq)+CO2(g)→Al2O3.xH2O(s)+2NaHCO3(aq)
The remaining sodium silicate present in the solution. On filtering, drying and heating of hydrated alumina gives Al2O3again.
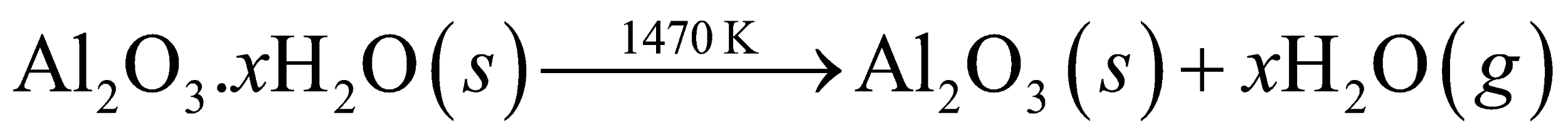
2)The next step is the dissolving of purified bauxite in cryolite. Now the electrolysis process takes place. The extraction is completed via way of means of electrolysis.
The resulting reaction is
Al2O3→2Al3++3O−
The reduction reaction occurs in cathode, 2Al3++6e−→2Al
The oxidation reaction occurs at anode, 3O−−6e−→3O
Cryolite and Fluorspar are introduced to lower melting point and increase conductivity of ore. So they are introduced to Bauxite for higher extraction of Aluminium.The use of cryolite also reduces a number of the energy costs included in extracting aluminium.
Hence, correct option is B
Note: Aluminium is the most abundant metal in the Earth's crust. It is costly due to the amount of power required in the extraction process.
