Question
Question: Draw the structure of the following compounds: (i) Ethanoic acid (ii) Bromopentane (iii) Butan...
Draw the structure of the following compounds:
(i) Ethanoic acid
(ii) Bromopentane
(iii) Butanone
(iv) Hexanal
Solution
The name of the structure of any compound in organic chemistry is determined by the rules of the nomenclature. It includes the long parent carbon chain rule, lowest number for the main functional group rule, maximum substituents rule and lowest number to the multiple bond rule.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us draw the structures of the given compounds with the help of rules of nomenclature as prescribed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
(i) Ethanoic acid: The compound name starts with ‘eth’ which signifies the maximum number of carbon atoms in the parent chain is two. The suffix ‘oic acid’ signifies that the main functional group in the organic compound is carboxylic acid. There are no multiple bonds and substituents present in the compound. Combining the data above, the structure of ethanoic acid is found to be:
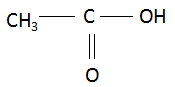
(ii) Bromopentane: The compound name starts with ‘pent’ which signifies the maximum number of carbon atoms in the parent chain is five. The suffix ‘ane’ signifies that there is no functional group present in the compound and the compound is a simple alkane. There are no multiple bonds and substituents present in the compound. Combining the data above, the structure of bromopentane is found to be:
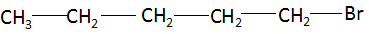
(iii) Butanone: The compound name starts with ‘but’ which signifies the maximum number of carbon atoms in the parent chain is four. The suffix ‘one’ signifies that the functional group present in the compound is a ketone. There are no multiple bonds and substituents present in the compound. Combining the data above, the structure of butanone is found to be:
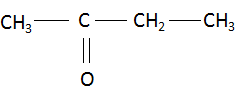
(iv) Hexanal: The compound name starts with ‘hex’ which signifies the maximum number of carbon atoms in the parent chain is six. The suffix ‘al’ signifies that the functional group present in the compound is an aldehyde. There are no multiple bonds and substituents present in the compound. Combining the data above, the structure of butanone is found to be:
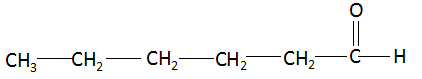
Note:
Although the compound bromopentane has various numbers of isomer due to the different positioning of the bromine atom, the priority of drawing the compound should be given to 1-bromopentane because the bromine atom which acts as a substituent in the compound receives the smallest numeric value. The other two isomers are: 2-bromopentane and 3-bromopentane.
