Question
Question: Draw the structure of \( \text{B}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}^{\text{-}} \) ion....
Draw the structure of BF4- ion.
Solution
The structure of a molecule can be determined from the hybridization of the central atom. Where hybridization refers to the intermixing of the atomic orbitals to form hybrid atomic orbitals that have mixed character of all the orbitals involved. We can find the hybridisation using the formula given below.
The hybridization of the central atom, H =2V + X - C + A
Where V is the number of electrons in the valence shell, X is the monovalent groups, C is the charge of the cation if it is cationic and A is the charge of the anion if it is an anionic species.
Complete Stepwise solution:
The central atom in the boron tetrafluoride anion is boron which has 5 electrons in total and has three electrons in the valence shell. The electronic configuration of Boron is: 1s22s22p1
For boron, the number of electrons in the valence shell is three, the monovalent groups are four, and the cationic charge is -1. Putting the values in the above equation is:
H =23 + 4 - 0 + 1=28=4
This means that there are four hybrid sp3 orbitals that are arranged in a tetrahedral arrangement. Hence the structure of BF4- is as follows:
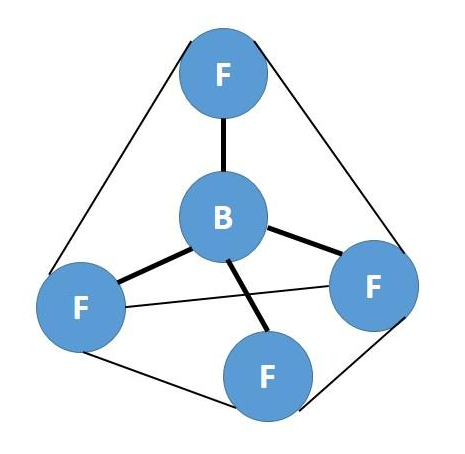
Note:
The hybridization of the atomic orbitals is an extension of the valence bond theory that influences the molecular geometry and the bonding properties of the elements. A classic example of hybridization is the bonding of carbon. It forms four bonds though it has two unpaired electrons in the initial ground state. The other two electrons in the 2s orbitals are unpaired to give rise to four unpaired electrons and it forms four covalent bonds.
