Question
Question: Draw the orbit structure to show the formation of the following: A.Oxygen molecule B.Ammonia ...
Draw the orbit structure to show the formation of the following:
A.Oxygen molecule
B.Ammonia
C.Calcium Oxide
(H = 1, N = 7, O = 8, Ca = 20)
Solution
The arrangement of all the electrons in an atom of an element or the molecule of a compound in all its orbits is known as the orbit structure of the element or the compound.
Complete answer:
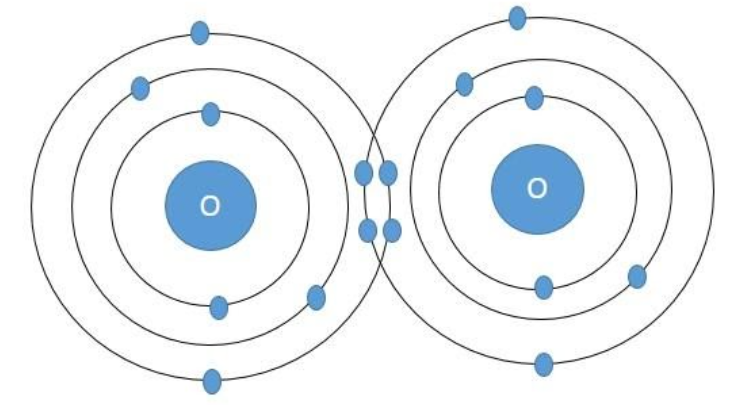
Oxygen molecule – In the atom of oxygen, there are total eight electrons arranged in the electronic configuration:1s22s22p4. Accordingly, there are a total of six electrons in the valence shell of the oxygen atom and it is short of two electrons to attain the octet confirmation. So the oxygen atom shares two electrons with another oxygen atom to form the oxygen molecule according to the following diagram.
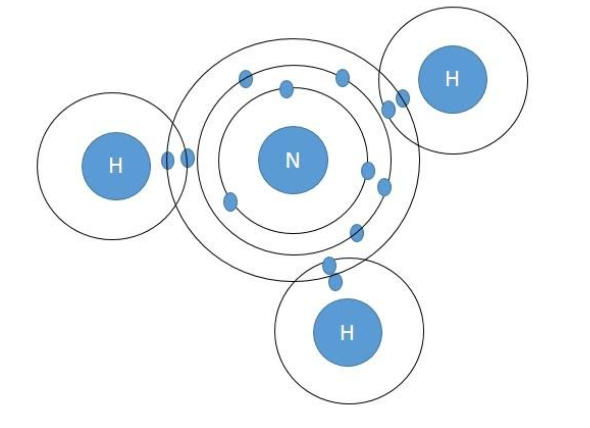
Ammonia – In the ammonia molecule, there is one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms. The electronic configuration of nitrogen is 1s22s22p3and that for hydrogen is1s1. Hence hydrogen is one electron short of duplet and nitrogen is three electrons short of an octet. So the nitrogen forms three covalent bonds with hydrogen atoms to form ammonia.
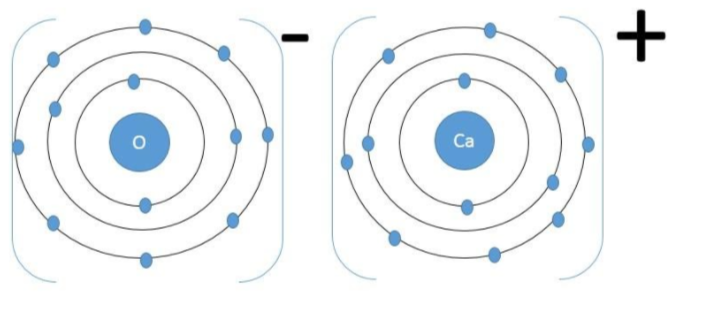
Calcium Oxide – The electronic configuration of calcium is1s22s22p63s23p64s2. So the calcium atom donates two of its valence shell electrons to form the calcium dipositive cation while the oxygen atom takes up those electrons to form the oxide anion and together they form the calcium oxide ionic solid.
Note:
The atoms gain or lose electrons to attain a stable electronic confirmation. But when the number of electrons required to attain the octet configuration is too large, then the atoms prefer to share the electrons and form covalent bonds instead of gaining or losing electrons.
