Question
Question: Draw the diagram representing the schematic arrangement of the Geiger-Marsden experimental setup for...
Draw the diagram representing the schematic arrangement of the Geiger-Marsden experimental setup for the alpha scattering.
Solution
Geiger-Marsden experiment or Rutherford scattering experiment is performed in order to know about the structure of atoms and to confirm if thomson’s pudding model of atom is correct. Here alpha particle rays are made to pass through thin gold foil and zinc sulphide screen placed around to get a flash of light when hit by an alpha particle. Many important conclusions are drawn from this experiment.
Complete answer:
The experimental setup consists of a source for alpha particles, lead bricks to ensure narrow beam passing through foil, very thin gold foil, zinc sulphide screen, detector to detect scattered alpha particles.
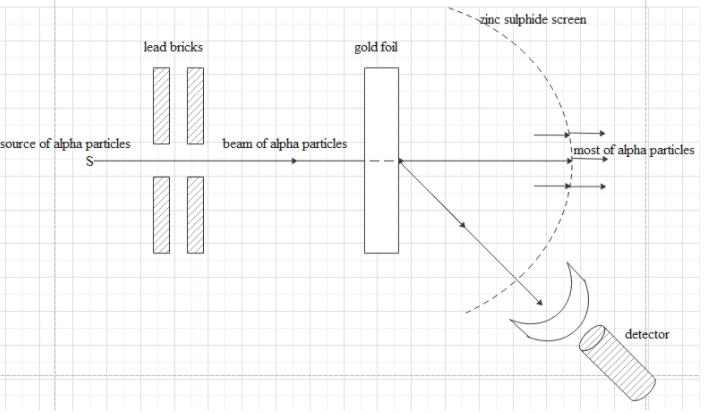
The gold foil used is nearly 0.0001 m thick.
Main observations from this experiment are
-very less number of alpha particles rebounded back
-some of them got scattered at random angles which are called scattering angles
most of the alpha particles passed through the gold foil.
-That scattering is also known as coulomb scattering as it happens due to the coulomb force of interaction.
-most of the space in atoms is empty.
-A high amount of positive charge is concentrated in a small compact area called nucleus and is surrounded by electron clouds.
Additional Information:
From this experiment Thompson pudding model i.e negatively charged electrons embedded in positively charged matter is proved to be wrong.
Note:
During scattering of an alpha particle the closest distance it can approach the nuclei and scatter is called closest distance of approach and it can be found by equating the initial kinetic energy of the alpha particle with the final coulomb interaction energy of the nucleus and alpha particle. At head on approach this distance is given by an upper limit of nuclear size which is of order 10−15.
