Question
Question: Draw the cis and Trans structures of\[hex - 2 - ene\]. Which isomer will have higher boiling point a...
Draw the cis and Trans structures ofhex−2−ene. Which isomer will have higher boiling point and why?
Solution
To answer this question first we need to know about the structure ofhex−2−ene. We also should know about how to draw cis and Trans structure of that compound (hex−2−ene).With regards to science, cis demonstrates that the useful gatherings are on a similar side of the carbon chain while trans passes on that useful gatherings are on opposite sides of the carbon chain. And we also know that boiling point is dependent on dipole dipole interaction. So, we need to know about how dipole dipole interaction works between the atoms of each molecule and how it is connected with boiling point.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of hex−2−ene is:
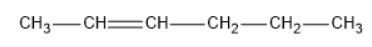
The two isomers obtained from hex−2−ene is below:
- Cis-isomer:
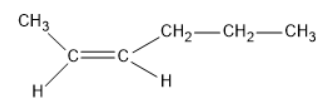
- Trans-isomer:
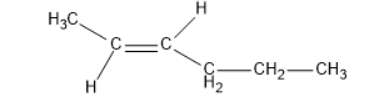
The dipole moment of cis-compound is an amount of the dipole moments of C-CH3 and C-CH2-CH2-CH3 bonds acting in a similar way. The dipole moment of trans-compound is the resultant of the dipole moments of C-CH3 and C-CH2-CH2-CH3 bonds acting inversely. Thus, cis-isomer is more polar than trans-isomer. The higher the extremity, the more noteworthy is that the inter atomic dipole-dipole connection, and therefore higher is going to be the limit.
Henceforth, the cis-isomer will have higher boiling point than the trans-isomer.
Note: Cis-trans isomers are stereoisomers, that is, sets of particles that have similar equations yet whose utilitarian gatherings are pivoted into an alternate direction in three-dimensional space. It isn't to be mistaken for E–Z isomerism, which is an absolute stereo chemical depiction. Stereoisomers contain double bonds that don't rotate, or they may contain ring structures, where the pivot of bonds is confined or prevented.
