Question
Question: Draw electron-dot representation for the formation of Magnesium oxide?...
Draw electron-dot representation for the formation of Magnesium oxide?
Solution
Magnesium oxide has magnesium and oxygen with the formula MgO. Mg is metal and O is a non-metal which means it forms an ionic bond. An ionic bond is formed by the electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions in a compound. Valence electrons are the number of electrons present in the outermost or valence shell. The metal shows a property of oxidation.
Complete step by step answer:
-First, let us learn the steps used to draw an electron dot structure.
-The first and foremost step that you have to do is to write the name of the central atom.
-The second step is to find out the atomic number of the central as well as neighbouring atoms and figure out the valence electrons present.
-Let us take magnesium oxide as an example. Now we have magnesium as the central atom.
-From the periodic table, we can find out that Mg is metal and O is a non-metal which means it forms an ionic bond.
-The atomic number of magnesium is 12. The electronic configuration is 1s22s22p63s2. The valence electrons are 2.
-Now the atomic number of O is 8 and the electronic configuration is 1s22s22p4. Thus the valence electrons present are 6.
-Now, the next step is to draw the valence electrons around the atoms.
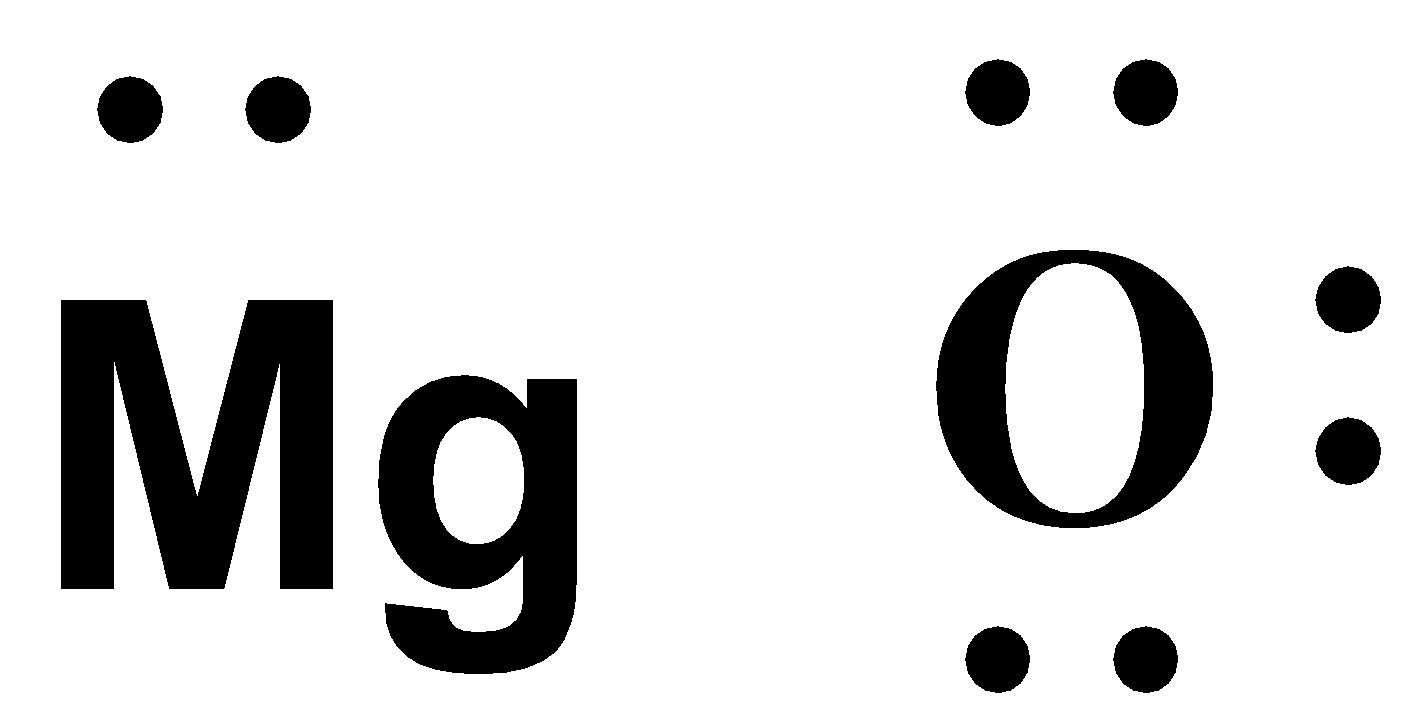
-We know that Mg is a metal. The metals are always oxidized. This means that it gives away its 2 valence electrons to Oxygen and gains a positive charge.
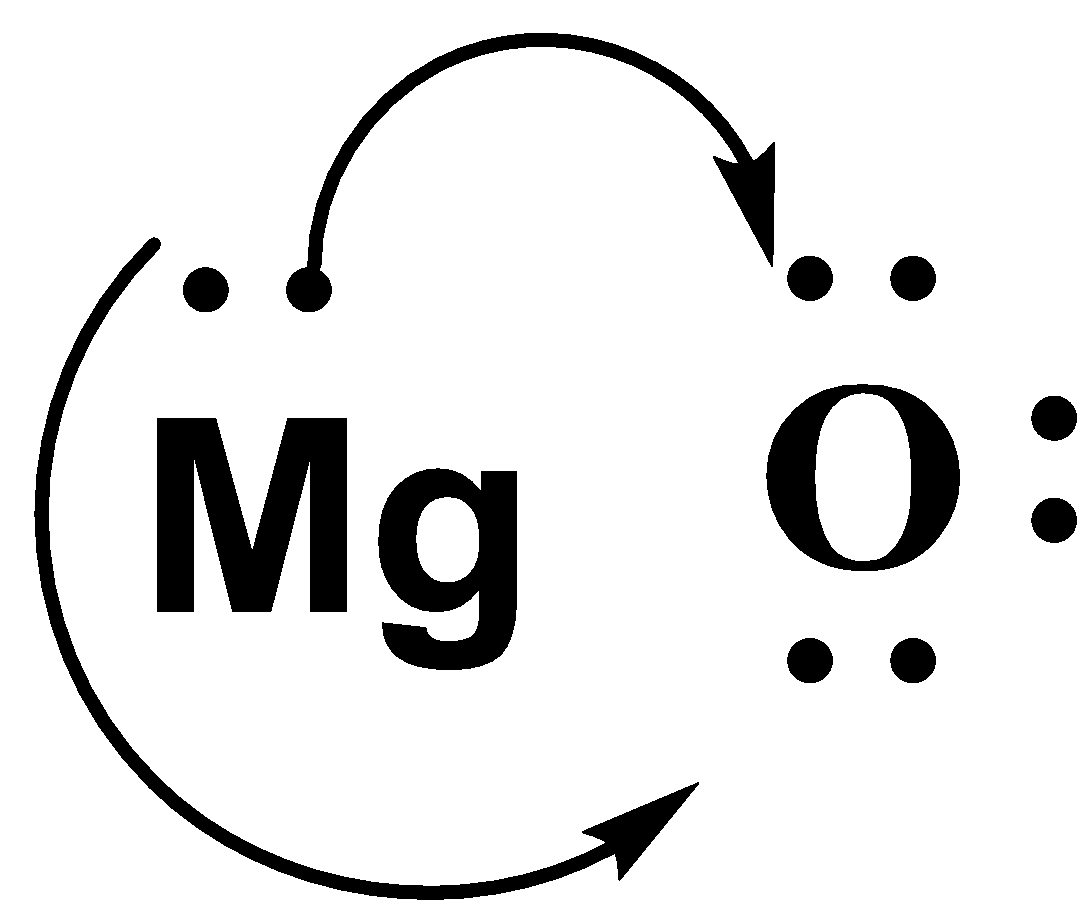
-The oxygen atom accepts the 2 electrons given by the Mg and gains a negative charge.
-So, we can say that there is an ionic bond between them due to the attraction between the positive and negative charge.
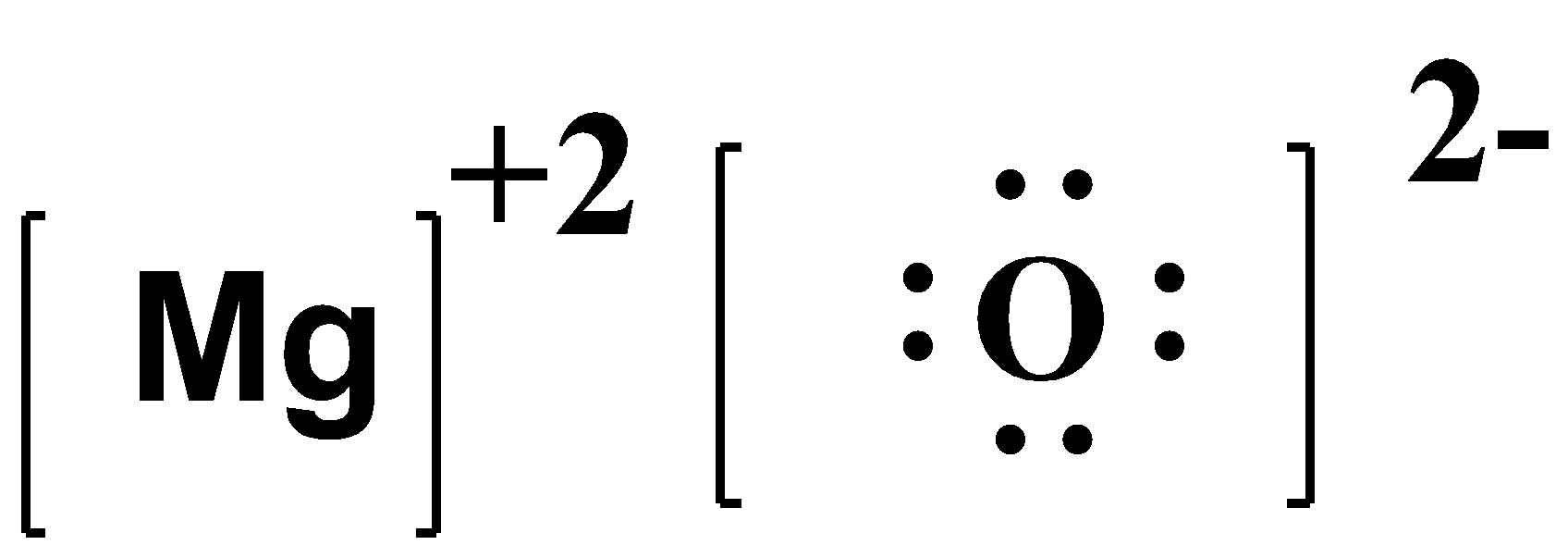
Note:
This was the electron dot structure of an ionic bond. The electron dot structure of almost all compounds can be drawn by assigning the central atom and the total number of valence electrons. Even though Lewis dot structures help in bonding, there are 3 exceptions- in electron-deficient molecules, expanded octets, and an odd number of electrons. The examples are SF4,NO2,BeCl3.
