Question
Question: Draw a rough sketch of the region \[\\{\left( x,y \right):{{y}^{2}}\le 3x,3{{x}^{2}}+3{{y}^{2}}\le 1...
Draw a rough sketch of the region (x,y):y2≤3x,3x2+3y2≤16 and find the area enclosed by the region using integration.
Solution
Start by drawing the diagram of the situation given in the question. If you observe, you will see that the inequality y2≤3x represents the region inside the parabola y2=3x and the inequality 3x2+3y2≤16 represents the area inside the circle with the center as the origin. So, to find the area use the method of definite integration. For limits of integration, find the x-coordinate of intersection of the boundaries of two regions represented by the inequalities given in the question. To make the question easier, just find the area of the region enclosed above the x-axis and double it to get the total area.
Complete step-by-step solution -
We know that the equation y2=3x represents a parabola with vertex at origin. So, the inequality y2≤3x represents the region inside the parabola y2=3x . Also, the equation 3x2+3y2=16 represents a circle with centre at the origin. So, the inequality 3x2+3y2≤16 represents the area inside the circle with centre as the origin and radius 316 .
Let us draw the representative figure of the situation given the question.
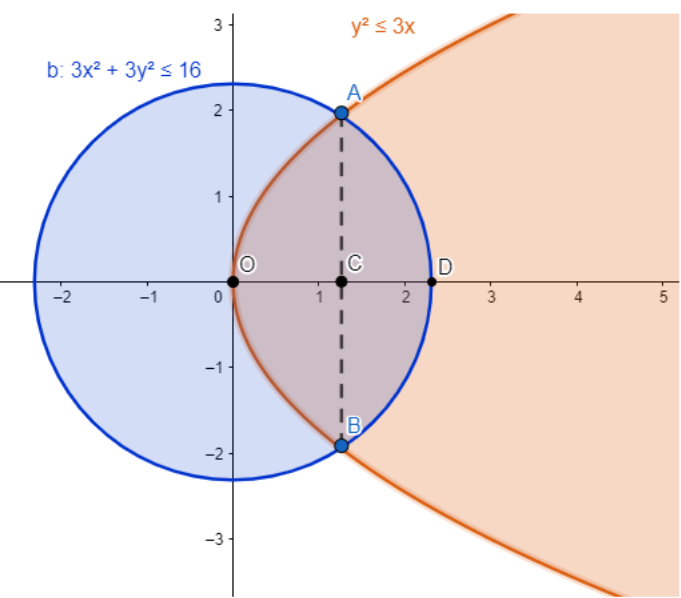
So, according to the question, we need to find the area of the region AOBD. We know that the given regions are symmetric about the x-axis, so to make the calculations easier, we will find the area above the x-axis, i.e., the area of the region AOD and double it to get the total area.
First, let us find the x-coordinates of the point A, which is the intersection of the curves y2=3x and 3x2+3y2=16 . so, let us substitute y2 from equation of parabola in the equation of circle, on doing so, we get
3x2+3y2=16
⇒3x2+3×3x=16
⇒3x2+9x−16=0
As the above equation is a quadratic equation, we will use the quadratic formula, and as x is positive we will only consider the positive value of x.
x=2a−b±b2−4ac=2×3−9±81+192=6−9±273
As the only positive value of x is to be considered, the x-coordinate of A is 6−9+273 .
Also, the x-coordinate of point D is equal to the radius of the circle, i.e., 316.
Now, to find the area of the region AOD, we need to use the method of definite integration. The equations are y2=3x⇒y=3x and 3x2+3y2=16⇒y=316−3x2. We know that the area bounded by any general curve y=f(x), in region x=a to x=b is given by a∫bf(x)dx .
ar(AOD)=0∫6−9+2733xdx+6−9+273∫316316−3x2dx
Now, we know that the integral of x is equal to 32x3 .
ar(AOD)=3×32x306−9+273+6−9+273∫316(316)2−x2dx
Now we know that ∫a2−x2dx=2xa2−x2+2a2sin−1ax+c.
ar(AOD)=3×2×3(6−9+273)3+(2x316−x2+616sin−1163x)6−9+273316
