Question
Question: Draw a rough sketch of the graph of the function \(y = 2\sqrt {1 - {x^2}} ,x \in \left[ {0,1} \right...
Draw a rough sketch of the graph of the function y=21−x2,x∈[0,1] and evaluate the area enclosed between the curve and the x-axis.
Solution
To solve this question, we will use the concept of application of integration. If the curve y=f(x) lies above the x-axis on interval [a,b], then the area bounded by the curve y=f(x), x-axis and the ordinates x = a and x = b is given by,
a∫b∣f(x)∣dx=a∫bf(x)dx=a∫bydx [∴f(x)⩾0 for all x∈[a,b]∴∣f(x)∣=f(x)]
Complete step-by-step answer:
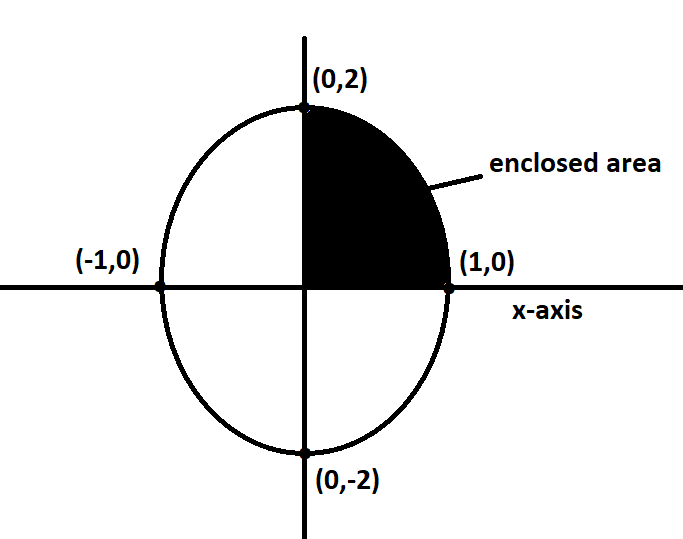
Given that,
y=21−x2,x∈[0,1]
Let us simplify this equation of curve in a simple form,
⇒y=21−x2 ……. (i)
Squaring both sides on equation (i),
⇒y2=4(1−x2)
⇒4y2=1−x2
⇒1x2+4y2=1
Here, we can see that this is the equation of an ellipse.
So,
⇒y=21−x2 will represent the portion of the ellipse lying in the first quadrant.
So, the required area A enclosed between the curve and the x-axis is given by,
⇒A=0∫1ydx
Putting the value of y,
⇒A=0∫121−x2dx ……… (ii)
As we know that,
∫a2−x2dx=21xa2−x2+2a2sin−1ax+C
If we compare a2−x2 with 1−x2,
We get a = 1.
So, the integration of equation (ii) will become,
⇒A=2[21x1−x2+21sin−11x]01
⇒A=2[(21(1)1−12+21sin−111)−(2101−02+21sin−110)]
⇒A=2[(0+21(2π))−0]
⇒A=2×4π
⇒A=2πsq. units.
Hence, the area enclosed between the curve and the x-axis will be 2π sq. units.
Note: Whenever we asked such type of questions, we should also remember that, If the curve y=f(x) lies below the x-axis on interval [a,b], then the area bounded by the curve y=f(x), x-axis and the ordinates x = a and x = b is given by,
a∫b∣f(x)∣dx=−a∫bf(x)dx=−a∫bydx [∴f(x)⩽0 for all x∈[a,b]∴∣f(x)∣=−f(x)]
