Question
Question: Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation by the combination of two thin convex lenses to conta...
Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation by the combination of two thin convex lenses to contact. Obtain the expression for the power of this combination in terms of the focal length of the lenses.
Solution
For this question we have to use the lens formula and power of lens formula. As two lenses are used, the image of the first lens will act as an object for the second lens. The principle and rules of ray optics are necessary for solving this problem.
Formula used:
Mirror formula- f1=v1−u1
Power of lens - P=f1
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider two lenses be L1, L2 having optical centres C1and C2 respectively. Let f1 and f2 be focal length of lens L1 and L2. Below is the ray diagram representing the path the light ray has travelled to form an image. The object is placed at O and passes through lens L1and L2forming an image at P then this image will act as an object for lens L2 and final image is formed at I.
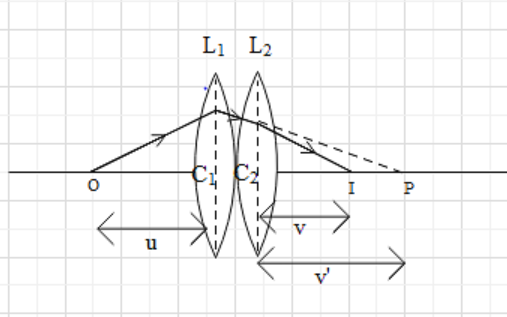
The distance between object O and C1is represented as u, distance between C2 and I is v and distance between C2 to P is v′.
Applying lens formula for convex lens L1
f11=v′1−u1…….. (1)
Similarly for lens L2,
f21=v1−v′1……... (2)
For the lens L2, P will act as virtual image object
Adding equation (1) and (2)
f11+f21=v1−u1
F1=f11+f21
Where, F be the focal length of the combined lens.
Power of lens is given by
P=F1
Therefore power of combined lens
P=f11+f21
Hence the answer has been calculated.
Note: The sign used in the formula should be taken care of properly. As two lenses are there, one should always solve for lens 1, the result of which will be used for lens 2. A ray diagram should always be drawn with a sharp pencil and the direction of the ray should be marked properly.
