Question
Question: Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image by a convex lens when an object is placed in fr...
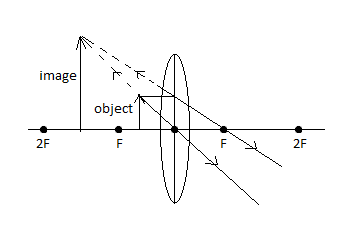
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image by a convex lens when an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus. Mention the nature of image formed.
Solution
Hint We can use the way of tracking the rays of light in a lens. The light is coming from the object in the form of rays and the image is formed at the point where the rays intersect after passing through the lens. If the rays after passing through the lens are diverging then it means that a virtual image is formed. If the rays are converging after passing through the lens then the image formed is real.
Complete step by step solution An image is formed after passing through a lens because of the bending of light due to the lens refractive index. For convenience sake, the following rays are considered for tracking the rays.
The ray that goes parallel to the principal axis, this ray bends and goes through the focal point after refracting. Let us consider this point as F.
The ray passing through the optic center (the center of the lens) this ray does not bend. Let us consider this center point as O.
The ray that goes through the focal point and gets refracted parallel to the optical axis
We trace these rays coming from the object and the point where these rays meet is where the image is formed. If the rays don’t meet and are diverging then the image is a virtual one.
In the case of a convex lens when the object is placed between F and O (focal point and optic center) the image formed is between Fand 2F on the same side as the object.
The image formed is virtual erect and magnified. The rays are going backward so the image is virtual.
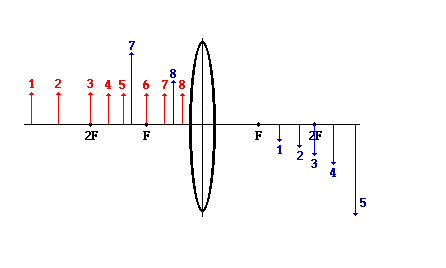
Note It might be noted from the above descriptions that there is a relationship between the object distance and object size and the image distance and image size. Starting from a large value, as the object distance decreases (i.e., the object is moved closer to the lens), the image distance increases, on the other hand, the image height increases.