Question
Question: Draw a neat labelled diagram of sectional view of mammary gland....
Draw a neat labelled diagram of sectional view of mammary gland.
Solution
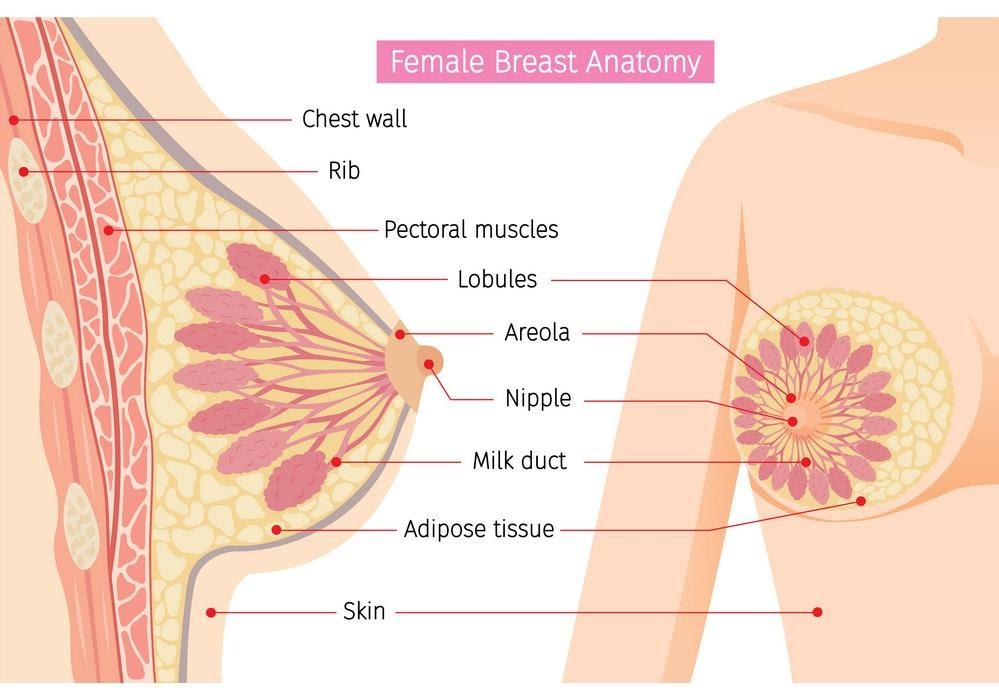
Mammary glands are exocrine glands present in mammals that produce milk to feed their children. The nipple, areola, ampulla, mammary lobe, mammary alveolus, mammary duct, ribs, and pectoralis muscle are all visible in this cross-sectional image of the mammary glands.
Mammary glands are glands that are found exclusively in animals. Exocrine and endocrine glands are the two types of glands. Exocrine glands are recognised for secreting their products through ducts, whereas endocrine glands lack ducts.
Complete answer:
The mammary gland is an exocrine gland because it has mammary ducts that release milk through the nipple. In primates, these glands serve as organs, udders in ruminants, and medications in other mammals.
When a female species is nursing her babies, these glands are solely capable of lactation.
A sectional image of the mammary glands reveals practically all of the gland's features, including the ribs and the pectoralis muscle. The mammary lobes and breast alveolus, which produce milk and are connected to specific mammary ducts that transport milk from the alveolus and lobe to the ampulla, are attached to them. The ampulla converges to produce the lactiferous duct, which eventually opens into the nipple, which is encircled by a darker skin patch called the areola.
Note:
The mammary gland is an exocrine gland that produces milk to nurse the infants of female mammals.
Males and females have the same ribs and pectoralis muscles.
Milk is created in the mammary alveoli and lobe and then flows to the duct, which then converges to form the ampulla and lactiferous duct.
The lactiferous duct emerges from the nipple, which is encircled by an area of darker skin known as the areola.
