Question
Question: Draw a neat labeled diagram of an animal cell....
Draw a neat labeled diagram of an animal cell.
Solution
Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that are protected by a cell membrane and include a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. But unlike eukaryotic cells of plants and fungus, the cells of animals don't even have a cell wall. Such a characteristic was already lost in ancient history by single-celled entities which have greatly contributed to the Kingdom Animalia.
Complete answer: The animal kingdom is remarkable amongst eukaryotic species since most animal tissues are fused together in a plasma membrane by a triple protein helix recognized as collagen. Plant and fungal cells are attached together by other substances, such as pectin, in tissue or clusters. The reality no other species employ collagen in this way is one confirmation that almost all animals originated from a single unicellular descendant. Bones, shells, spicules, and other rugged frameworks are shaped whenever the outer layer incorporating collagen between animal cells is calcified. Almost all animal cells are diploid that means that the chromosomes remain in homologous pairs. The distribution of animal cells emerges in a number of ways. Mostly in the case of sexual reproduction, the cell phase of meiotic division is first employed to produce haploid daughter cells or gametes. Two haploid cells merge to produce a diploid zygote, which turns into a new offspring as its cells are dividing and multiplying.
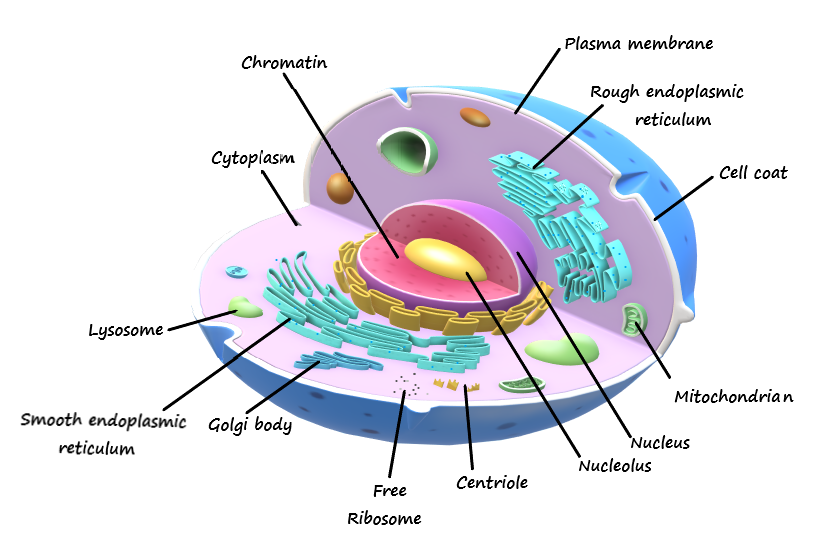
Additional Information:
Animal cells do possess structures such as centrioles, lysosomes, cilia, and flagella which were not usually found in plant cells. The centromeres are microtubule-organizing cores situated near the nucleus of animal cells. In accordance with their function as just a gastrointestinal component and organ-recycling Centre for animal tissue, lysosomes are regarded to be part of the endomembrane system.
Note: Animal cells exist in all forms and sizes, with dimensions varying from a few mm to m. Animals are smaller and simpler than plant cells and therefore are usually irregular in shape, taking various forms due to its lack of a cell wall. Acting together all cells allows the animal its flexibility to shift, replicate, adapt to stimuli, consume, and absorb food. Generally, the concerted effort of all animal cells might be what promotes the daily functioning of the body.
