Question
Question: Double bond equivalent (degree of unsaturation) of (A) is:  of (A) is:
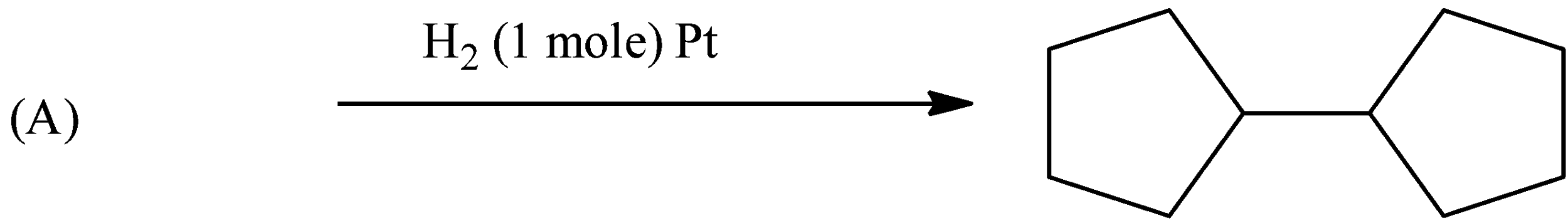
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Solution
The degree of unsaturation or Double bond equivalent tells the number of double bonds and the number of rings in the compound. If one mole of hydrogen is used then one double bond is present if 2 moles of hydrogen are used then 2 double bonds are present and so on.
Complete answer:
The degree of unsaturation or Double bond equivalent tells the number of double bonds and the number of rings in the compound. An unsaturated hydrocarbon contains either a double bond or a triple bond. When these unsaturated hydrocarbons are treated with hydrogen in the presence of metals like nickel, palladium, platinum, etc, the double bond or triple bond will get converted into a single bond by the addition of hydrogen atoms to the carbon atoms having the double bond.
The double bond equivalent can be calculated with the number of moles of the hydrogen gas used in the reaction. If one mole of hydrogen is used then one double bond is present if 2 moles of hydrogen are used then 2 double bonds are present and so on.
So, in the given reaction, the reactant is treated with 1 mole of H2, therefore, one-mole hydrogen will saturate one double. Hence, the compound (A) will have one double bond in between the cyclopentane. Therefore, the double bond equivalent will be equal to the number of double present in the compound and the number of rings present in the compound. So, there are 2 rings and one double bond, therefore, the double bond equivalent will be 3.
A correct answer is an option (c)- 3.
Note:
We can directly fine the double bond equivalent of a compound by the formula:
C+1−2H−2X+2N
Where C is the number of carbon atoms, H is the number of hydrogen atoms, X is the number of halogens, and N is the number of nitrogen present in the compound.
