Question
Question: Do water molecules leave or enter a cell in an isotonic solution?...
Do water molecules leave or enter a cell in an isotonic solution?
Solution
The word isotonic is further made up from two words. The first word is “iso” which means the same and the other word is “tonic” which means concentration. So, the meaning of the word isotonic is a liquid having the same concentration of liquid. So, we can say that an isotonic solution refers to a solution which is having equal concentration inside and outside.
Complete solution:
Isotonic solution is the solution having the same osmotic pressure. Isotonic solution maintains an electrolytic balance which is very much similar to the plasma in the main bloodstream. When an isotonic solution is poured, then the volume of the fluid of the patient is increased. The most common example of isotonic solution is 0.9% of saline and lactated ringers.
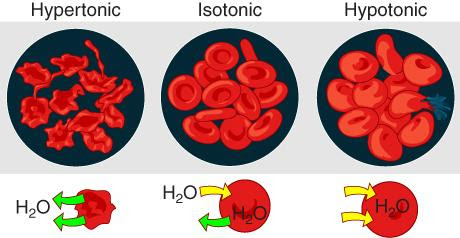
So, if a cell is placed in an isotonic solution, it means that we have placed a cell in the solution which is quite similar to the cell's solution. Hence, there will be no net movement of molecules which is taking place across the membrane and there will also not be any kind of net change in the concentration of the solvents as well as the solutes on both sides of the membrane. Any kind of diffusion or any kind of osmosis will not take place as the equilibrium has already been achieved. There will be a free movement of water molecules across the membrane without any change in the concentration of solutes on each of the sides, in case of an isotonic environment.
Thus, the water molecules will leave as well as enter the cell during this process.
Note:
It is important to note that an isotonic solution is the solution that has the same concentration as it is of another given solution. If these two solutions are separated by a semipermeable membrane, then the solution will flow in equal parts as the concentration of solute and solvents are the same. This further allows the free movement of the ions and the molecules across the membrane and at the same time, concentration of solutes on either side is not disturbed.
