Question
Question: DNA is a polymer of a A. Glucose B. Amino acid C. Nucleotide D. None of the above...
DNA is a polymer of a
A. Glucose
B. Amino acid
C. Nucleotide
D. None of the above
Solution
DNA is the genetic material for all living organisms. It is a polymer. It contains sugar, nitrogenous bases, and phosphate groups. Cellulose is a polymer of glucose and proteins are the polymer of amino acids.
Complete answer: DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA stands for ribonucleic acid, both of them acts as genetic material for living organisms. DNA is more stable than RNA.
DNA is a long polymer of deoxyribonucleotides, therefore the length of the DNA is defined as the number of nucleotides. DNA is a double-stranded structure. A pair of nucleotides is called base pairs which are always complementary to each other.
A nucleotide is made up of three main components, these are sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. When a nitrogenous base is linked to a pentose sugar, it forms a nucleoside. The bond which connects them is N – glycosidic linkage.
A phosphate group is linked to the nucleoside by phosphodiester linkage to form a nucleotide at 5’ – OH group. 3’ - 5’ phosphodiester linkage connects two nucleotides, therefore it forms a long polymer called DNA.
Adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine, and uracil are the nitrogenous bases that are present in the DNA. Thymine is present in DNA and uracil replaces thymine in RNA when transcription is carried out in the cell. Thymine is also called 5 – methyl uracil.
Adenine pairs with thymine/uracil by two hydrogen bonds and guanine pairs with cytosine with three hydrogen bonds. This is called complementary base pairing. The ratios between adenine and thymine, guanine, and cytosine are constant and equal to one, this fact was stated by Erwin Chargaff and hence called Chargaff’s rule.
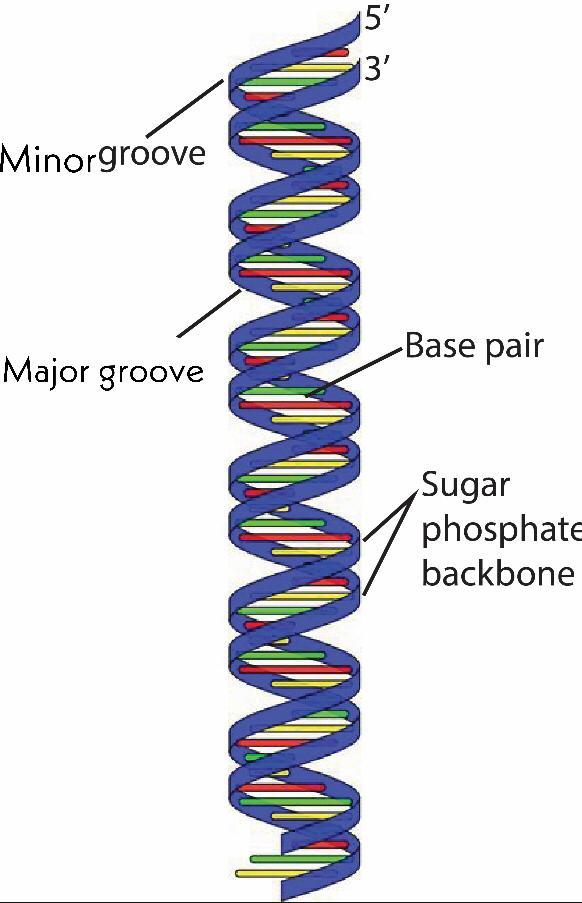
A double helix DNA is made up of two polynucleotide chains with antiparallel polarity where sugar-phosphate acts as the backbone and the nitrogenous bases project inside.
In a B – DNA the two chains are coiled in a right-handed fashion. In every turn of DNA, there are 10 base pairs, where the distance between the two bases is 0.34 nm. The pitch of the double helix model of the DNA is 3.4 nm or 34 Angstrom.
In the diploid content of human DNA, there are 6.6 x 109 base pairs. Therefore the total length of the haploid content of human DNA is 2.2 meters. DNA is packed as nucleosomes in the nucleus.
DNA is negatively charged, and it is wrapped around positively charged basic proteins called histones which are rich in basic amino acids like lysines and arginines. A histone octamer is formed of eight molecules of histones.
Hence, the correct answer is an option (C).
Note: In prokaryotes, there is a region called a nucleoid where DNA is held with some proteins which are positively charged. This happens because there is no nucleus in a prokaryotic cell-like bacteria.
In eukaryotes, nucleosomes become the repeating unit of a structure in the nucleus called chromatin and then its packaging at higher levels creates chromosomes with the help of some special proteins.
