Question
Question: Distinguish between tetrahedral voids and octahedral voids....
Distinguish between tetrahedral voids and octahedral voids.
Solution
Voids can be two dimensional or three dimensional. Both tetrahedral voids and octahedral voids are three-dimensional voids but they differ with each other in their size, a number of neighbouring atoms along with a void and also with respect to the ratio of cation and anion in the crystal lattice.
Complete step by step solution:
-Repetitive arrangement of the particles in a 3-D space is called a lattice. Usually, anions are aligned in a lattice and cations are present in the spaces between the anions. There are spaces left inside the lattice due to the structure of the atoms placed in it. These empty spaces are called voids.
-Since cations are smaller and anions are larger, voids become easy to form even though the packing efficiency of the lattice increases. Lesser the packing efficiency, more are the voids present in the crystal structure.
-The type of void present between the atoms of the lattice depends on the ratio of the size of cation and anion and different voids can be shown as
| Cation to anion ratio (R) | Type of void occupied |
|---|---|
| R<0.155 | Linear |
| 0.155 | Triangular |
| 0.225 | Tetrahedral |
| 0.414 | Octahedral |
| 0.732 | cubical |
-So, we can summarise the difference between the tetrahedral and octahedral voids as follows:
| TETRAHEDRAL VOIDS | OCTAHEDRAL VOIDS |
|---|---|
| Tetrahedral voids are the voids that are present in lattice structures where the coordination number of compounds is 4 | Octahedral voids are the voids that are present in lattice structures where the coordination number of compounds is 6 |
| It is simply a triangular void formed when a second layer of the lattice spheres are placed on the triangular void present between 3 atoms | It is formed in 2 ways. One way is by placing 2 arrangements of 3 spheres on top of each other. Another way is by placing 2 spheres on top and bottom of a square lattice of spheres respectively |
| The cation to anion ratio for this void is 0.225 | The cation to anion ratio for this void is 0.414 |
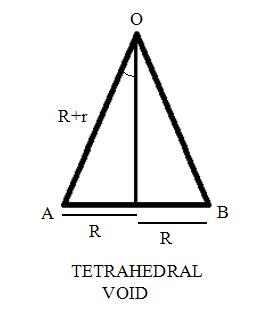 | 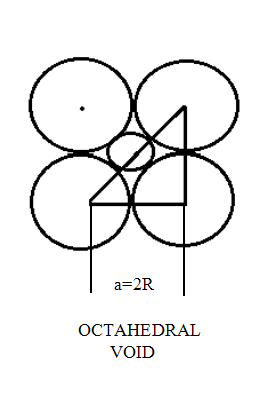 |
Note: Sodium chloride and the structures of such types form the octahedral voids in the crystal lattice. Zinc chloride and its related structures form the tetrahedral voids in the crystal lattice. Sometimes the cations and anions enter the void from the lattice and it is called defect in the crystal lattice.
