Question
Question: Discuss the principle and action of a Bainbridge mass spectrometer to determine the isotopic masses....
Discuss the principle and action of a Bainbridge mass spectrometer to determine the isotopic masses.
Solution
There are two types of fields used in Bainbridge mass spectrometer, electric and magnetic fields. Only ions having particular velocity are allowed to enter through the velocity selector. The force due to the magnetic field does not work, it only changes the direction of the moving particle.
Complete step-by-step solution:
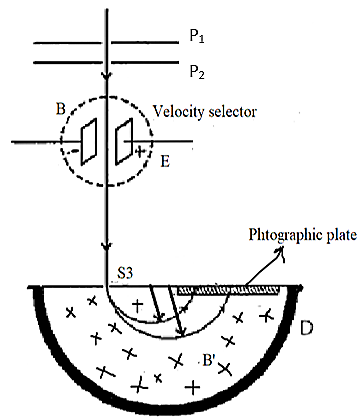
An instrument called Bainbridge mass spectrometer is used for the determination of atomic masses. If one or more electrons are removed from the atom then it has a net positive charge and it becomes a positive ion. Using two narrow slits S1 and S2, a beam of positive ions produced in a discharge tube is collimated into a fine beam. This fine beam then enters into a velocity selector. Only the ions of a particular velocity are allowed to come out from the velocity selector. The velocity selector consists of two plane parallel plates P1 andP2, which produces a uniform electric field, it also has an electromagnet which produces a uniform magnetic field. These electric and magnetic fields are at right angles to each other and to the direction of the beam.
The electric field and magnetic field are so adjusted in such a way that the deflection produced by one field is nullified by the other so that the ions do not suffer any deflection within the velocity selector.
Let E be the electric field intensity, B be the magnetic induction respectively and q be the charge on the positive ion.
The force exerted by the electric field is
FE=qE
The force exerted by the magnetic field is
FB=qvB
Where v is the velocity of positive ions.
We have,
FE=FB
∴qE=qvB∴v=BE
The ions having this velocity are allowed to pass through the velocity selector. Then they pass through a slit S3 and then they enter in evacuated chamber D. The positive ions having the same velocity are again influenced by another strong uniform magnetic field of induction at right angles to the plane of the paper acting inwards. These ions then move in a circular path of radius R and strike the photographic plate. The centripetal force is provided by this magnetic field. Therefore,
