Question
Question: Dihalogen derivative (A) of a hydrocarbon having two carbon atoms reacts with alcoholic potash and f...
Dihalogen derivative (A) of a hydrocarbon having two carbon atoms reacts with alcoholic potash and forms another hydrocarbon which gives a red precipitate with ammoniacal cuprous chloride. Compound A gives an aldehyde when treated with aqueous KOH. Write down the name and formula for the organic compound.
Solution
When we boil the geminal dihalides with aq. KOH or aq.NaOH. It gives aldehydes and ketones as a product. So we can use the above information to solve this question.
Complete step by step answer:
Following is the summary of question,
Dihalogen derivative(2C)+alcoholicpotash→hydrocarbon product ………………………………. (1)
From equation 1,
Hydrocarbon product + Ammoniacal cuprous chloride → substance that forms Red precipitate
Again from equation 1,
Dihalogen derivative(2C)+aq.KOH→Aldehyde
And it has been asked to find the name and formula of dihalogen derivative.
So, the compound A is the dihalogen derivative of hydrocarbon. Again it has mentioned that the compound is a 2-carbon compound. So, let’s assume that the two carbon containing hydrocarbons with two halogen group are geminal dihalides (CH3−CH−X2) having two halogen atoms situated on a terminal carbon atom.
So, considering halogen X as chlorine, the CH3−CH−X2 is 1-1- dichloroethane, which is geminal dihalides that react with KOH and produce an unstable hydroxyl compound. This hydroxyl compound on water molecule loss yields acetaldehyde (CH3−CHO)
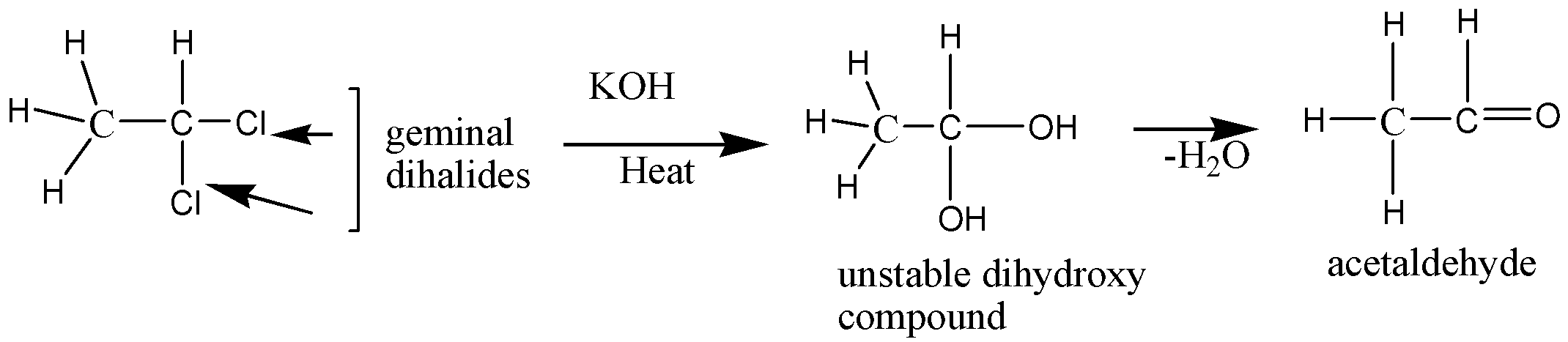
This geminal dihalide of 1-1- dichloroethane when reacts with alcoholic KOH or potash undergoes the dehydrohalogenation process and yields CH≡CH, acetylene or ethyne
Acetylene or Ethyne in presence of ammoniacal cuprous chloride forms a red-brown colored precipitate of 1,3-Butyne.
So, Compound A is 1,1 dichloroethane whose chemical formula is CH3−CH−Cl2
Note:
We must know that the Glaser coupling test is the identification test for terminal alkynes, where terminal alkyne reacts with ammoniacal cupric chloride which on subsequent oxidation in air gives di-yne.
