Question
Question: Differentiate between monocot and dicot with three examples. Draw necessary diagrams....
Differentiate between monocot and dicot with three examples. Draw necessary diagrams.
Explanation
Solution
Comparison is done on basis of definition, leaves, vascular bundle, root system, stomata, secondary growth, secondary cambium, vascular bundles in stem, venation in leaves.
Complete answer:
| Basis: | Monocot | Dicot |
|---|---|---|
| Definition: | Plants having one cotyledons in seeds are monocots | Plants which have two cotyledons in seeds are dicots.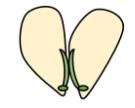 |
| Venation: | Monocot leaves have parallel venation. | Dicot leaves have reticulate venation |
| Stomata: | Stomata are present on both the upper and lower epidermis of leaves | Stomata are present more on the lower surface of leaves |
| Root system: | Monocots tend to have fibrous root system | Dicots have tap root system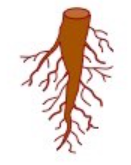 |
| Leaves: | Dorsiventral leaves are present | Isobilateral leaves are present |
| Stem: | Vascular bundles are scattered in stem | Vascular bundle are present in ring in the stem |
| Secondary cambium: | Secondary cambium is absent in monocots | Secondary cambium is present in dicots |
| Secondary growth: | Secondary growth does not occur in monocots | Secondary growth occurs in dicots |
| Examples: | Examples: Sugarcane, wheat, rice etc | Examples: Mango, tomato, lettuce etc. |
Note: Plants with one cotyledon are monocot and plants with two cotyledons are called dicot. You can also mention that the floral parts of monocot are in multiples of three and dicot is four or five.
