Question
Question: Diameter of a plano-convex lens is 6 cm and thickness at the centre is 3mm. If speed of light in mat...
Diameter of a plano-convex lens is 6 cm and thickness at the centre is 3mm. If speed of light in material of lens is 2×108 ms−1, the focal length of the lens is,
(A). 15 cm
(B). 20 cm
(C). 30 cm
(D). 10 cm
Solution
Try to understand the concept of lens. Study the lens maker’s formula and try to know a little about the geometry of a circle. Refractive index is the ratio of velocity of light in vacuum to velocity of light in the medium.
Formula Used:
f1=(μ−1)×(R11−R21)
Complete step-by-step answer :
We have a plano-convex lens.
We have the speed of light in the material as v=2×108ms−1
Hence, the refractive index of the lens material will be,
refractive index, n=vc=2×108ms−13×108ms−1=1.5
Now, consider the lens as a part of the complete circle as shown in the diagram.
Here, AB = 6 cm
Hence, AE = BE = 2AB=26cm=3 cm
DE = 3 mm = 0.3 cm
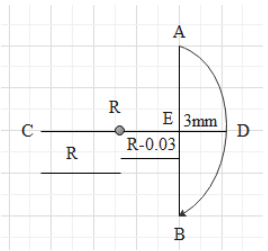
The lens is a part of a sphere. So, we can draw it as,
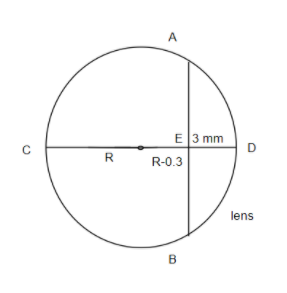
First, we have to find the radius of curvature of the circle.
We know that in a circle if two line intersect each other perpendicularly then we have,
BE × AE = CE × DE3×3=(R+R−0.3)×0.3⇒2R−0.3=0.39⇒2R=30+0.3⇒2R=30.3⇒R=230.3⇒R=15.15 cm⇒R≈15 cm
Hence, radius of curvature, R = 15 cm
Now we have the refractive index and the radius of curvature of the lens.
To find the focal length we will use the lens maker’s formula.
f1=(μ−1)×(R11−R21)⇒f1=(1.5−1)×(151−∞1)⇒f1=0.5×(151−0)⇒f1=150.5⇒f1=301⇒f=30 cm
So, the focal length of the plano-convex lens will be 30 cm.
The correct option is C.
Note : You should know which formula could be used in a particular solution. Here velocity of light in the material is given. Also, we have data to find the radius of curvature of the lens. So, we used the lens maker’s formula.
Here, R2 is infinity because for a plane mirror we don’t have a radius of curvature. Its focus will be at infinity and radius of curvature is also infinity. For a plano-convex lens one side is a plane lens. That’s why we used R2 as infinity.
