Question
Question: Determine the minimum value of current gain \(\beta \) (up to nearest integer) required to put the t...
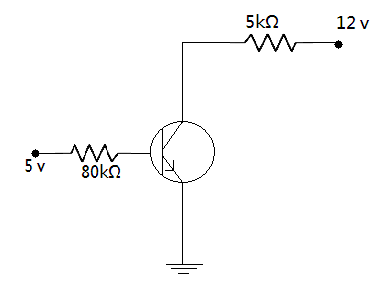
Determine the minimum value of current gain β (up to nearest integer) required to put the transistor in saturation when VBB=+5V . Assume that in saturation state, VBE=0.8V and VCE=0.12V.
Solution
In this problem we need to find the value of current gain. Current gain is the ratio of the collector current to the base current. In order to find the collector current and the base current, apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law in the base-emitter loop and in the collector loop.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us understand current gain and voltage gain first. The current gain in the common-base configuration is defined as the change in collector current divided by the change in emitter current, when base-to-collector voltage is constant. Similarly, the voltage gain for the common base amplifier is the ratio of output voltage to the input voltage.
Let IB and IC be base current and collector current respectively, taking +5V as input voltage Vin , the summation of voltages in the base-emitter loop gives
8×103×IB+VBE−5V=0
We assume that the transistor is in saturation, this implies
VBE=VBE(sat)=0.8V
⇒8×103×IB+0.8V−5V=0
⇒IB=80×1034.2V=0.0525mA --equation 1
The base current is 0.0525mA
Applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law in the collector loop, we have
⇒5×103×IC+VCE−12V=0
We assume that the transistor is in saturation, this implies
VCE=VCE(sat)=0.12V
Substituting this value in the above equation, we get
⇒5×103×IC+0.12V−12V=0
⇒IC=5×10312−0.12=2.376mA
The emitter current is 2.376mA
The current gain is given as
β=IBIc
Substituting the values, we get
β=0.05252.376≈45.25
The minimum value of current gain β (up to nearest integer) is 45.
Note: In saturation mode, the transistor acts like a short circuit between the collector and the emitter. In saturation mode both the diodes in the transistor are forward biased. Be careful of the sign conventions when applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law. Remember that the current gain is the ratio of the collector current to the base current.
