Question
Question: Determine the bond order of the \(C - O\) bond in the following molecules, and then arrange the \(C ...
Determine the bond order of the C−O bond in the following molecules, and then arrange the C−O bond lengths in increasing order? CO, CO+ ,CO2+ ,CO2 ,CO32−.
Solution
For this question we should know about bond order, bond length and relation between them. As we know that the shorter the bond length, the stronger will be the bond and the stronger the bond, higher will be the bond order. So this implies that shorter the bond length, higher will be the bond order.
Formula Used:
Bond order (BO) = 21(Bondingelectrons−Antibondingelectrons)
Complete answer:
Bond Order of the compound is the half of the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons as shown in the formula. So with the help of Molecular Orbital Diagram, we can find out the total number of bonding and antibonding electrons present in the given compounds, i.e. CO, CO+ ,CO2+ ,CO2 ,CO32− .
Molecular Orbital Diagram of CO :
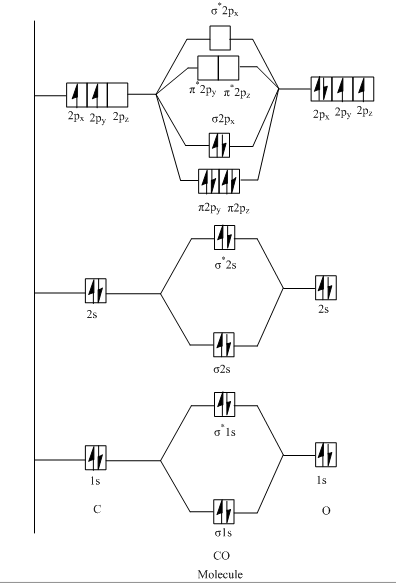
From above diagram, it is clear that number of bonding electrons is six (present two electrons in 2σ , 4 in 1π and 2 in 3σ ) whereas number of antibonding electrons is two (present in 2σ∗ ).
So the bond orders of CO is:
BO= 21(bondingelectrons−antibondingelectrons)
⇒21([2+2×2+2]−[2])
⇒3
Now, for CO+ Cation, we know that one electron is removed from a bonding MO. Then the bond order will decrease. So by using the same formula we get a bond order of CO+ is 2.5 .
For CO2+ Dication, it has one more electron removed from CO+ , so the bond order is 2 .
For CO2 molecule, the structure of CO2 :
So, it has double bonds and hence has a bond order of 2 .
For carbonate anions, we should consider resonance delocalization. The structure of CO32− :
Here, there will be 2π electrons delocalized onto three bonds, by making an average of 32 of a π electron, giving a π bond order of 31 . Where σ bonds have a bond order of 1 , the total bond order of carbonate anion is 1.33 .
Since the higher the bond order, the shorter the bond length will be, so the increasing order of the given compounds according to their bond length is:
rCO<rCO+<[rCO2+=rCO2]<rCO32−
Note:
Bond order was invented by Linus Pauling, and is defined as the difference between the number of bonds and antibonds. The bond number itself is the number of electron pairs between a pair of atoms.
