Question
Question: Describe the structure of the human brain....
Describe the structure of the human brain.
Solution
The brain is made up of many specialized areas that work together. It controls the functioning of vital involuntary organs, balance of body, movements, hunger, thirst, thermoregulation, circadian rhythm, endocrine gland activities, human behavior etc.
Complete answer:
In our body, the brain is the central information processing organ of our body and it acts as the command and control system. It is the site for processing of vision, hearing, speech, memory, intelligence, emotions and thoughts.
The human brain is well protected inside the skull. Inside the skull, the brain is covered by cranial meninges. Cranial meninges consist of three layers. Outer layer is called dura mater. Middle layer is very thin called arachnoid. Inner layer is called pia mater, which is contact with brain tissues.
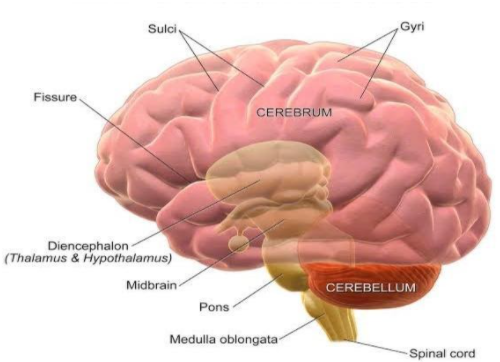
The brain is divided into three parts, forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain. The forebrain consists of cerebrum, thalamus and hypothalamus. Cerebrum forms the major part of the human brain. There is a deep cleft that can divide cerebrum longitudinally into two halves, which are termed as the right and left cerebral hemisphere. There is a tract of nerve fibers called corpus callosum, which connect the hemispheres.
The layer of cells which covers the cerebral hemisphere is called cerebral cortex and it is in the form of prominent folds. The cerebral cortex is known as the grey matter because it is greyish in appearance. Here the neuron cell bodies are concentrated to give this color. The cerebral cortex contains motor areas, sensory areas and large regions that are neither clearly sensory nor motor in function. These regions are called association areas. They are responsible for intersensory associations, memory and communication.
Inner part of the cerebral hemisphere contains fibers of tracts, which are covered with myelin sheath. The give an opaque white appearance to the layer and is called white matter.
The cerebrum wraps around a structure called, which is a major coordinating center for sensory and motor signaling. Hypothalamus lies at the base of thalamus. Hypothalamus contains a number of centers which control body temperature, urge for drinking and eating. It also contains several groups of neuro secretory cells, which secrete hypothalamic hormones. Inner parts of the cerebral hemisphere and a group of associated structures such as amygdala, hippocampus etc. form a complex structure called the limbic lobe or limbic system.
Along with the hypothalamus, limbic system involved in the regulation of sexual behavior, expression of emotional reactions (pleasure, excitement, rage and fear) and motivation.
The midbrain is located between the thalamus of the forebrain and pons of hindbrain. Cerebral aqueduct, which is a canal that passes through the midbrain. Midbrain and hindbrain constitute brainstem. The Dorsal portion of midbrain consists of four round swellings or lobes called corpora quadrigemina.
The hindbrain consists of pons, cerebellum and medulla oblongata. The fiber tracts that interconnect different regions of the brain, constitute pons. Cerebellum is a very convoluted surface in order to provide the additional space for many neurons. The medulla oblongata is connected to the spinal cord. Medulla contains centers which control gastric secretions, cardiovascular reflexes and respiration.
Note: The neural system coordinates and integrates functions as well as metabolic and homeostatic activities of all organs. Human neural system consists of two parts, the central neural system (CNS) and peripheral neural system. Central neural system contains the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral neural system contains all nerves associated with CNS.
