Question
Question: Describe the structure of a dicot seed....
Describe the structure of a dicot seed.
Solution
Within the seed cover, monocots only have one seed leaf. It is also just a small leaf, so the endosperm is not within the seed leaf to feed the young plant. Within the seed cover, dicots have two seed leaves. Typically, since they contain the endosperm to feed the embryo plant, they are rounded and fat.
Complete answer:
A seed coat is replaced by a dicotyledonous seed. Two membranes, an outer testa and an inner tegmen, compose a seed coat. The seed coat, called the hilum, has a scar on it. The growing seeds are attached to the fruit through the hilum. The tiny pore located just above the hilum is a micropyle. The seed coat encloses an egg. The fetus is composed of an embryonic axis and two cotyledons. The cotyledons are fleshy, and they act as the embryo's forming food reserves. The radicle and the plumules are at the two ends of the embryonic axis.
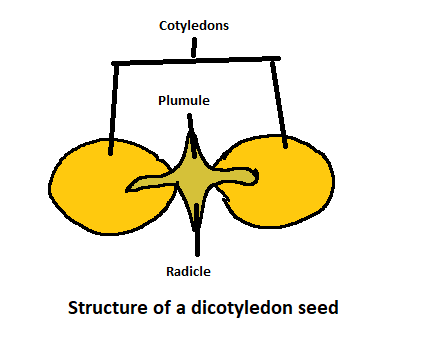
Examples of dicotyledon or dicot seeds include peas, almonds and cashews. Sometimes classified as dicots, dicotyledons are the classes into which were formerly split all the flowering plants or angiosperms. The term dicotyledons refer to the two embryonic cotyledons in the crop.
Note: Sometimes classified as dicots, dicotyledons are They are the classes into which were formerly split all the flowering plants or angiosperms. The term dicotyledons refers to the two embryonic cotyledons in the crop. To date, about 200,000 specimens of dicotyledon have been found.
