Question
Question: Describe the structure and function of the nephrons....
Describe the structure and function of the nephrons.
Solution
Nephron is the unit of the kidney which assists with cleaning and detoxifying our body. Amassing of harmful substances can even prompt passing. This is the explanation dialysis is performed when the kidneys of an individual are coming up short. A solitary solid kidney can likewise assist us with making due for the duration of our life.
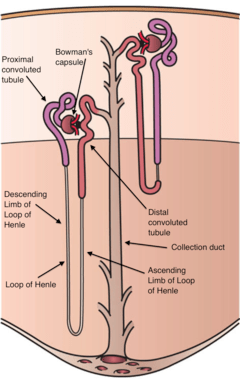
Complete answer:
The nephron is the primary and useful unit of the kidney. It consists of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle has two sections: glomerulus and a Bowman's case. A solid grown-up has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons for each kidney. Blood is separated as it goes through three layers-the endothelial cells of the fine divider, its storm cellar film, the podocytes of the coating of the case. There is a greatest reabsorption of the relative multitude of minerals and substances that are not to be flushed out. Toward the finish of the tubule, pee is flushed out which is made out of water, metabolic waste, and poisons.
Allow us to consider the various pieces of the nephron. Bowman's capsule is a cup-like sac toward the start of the nephron. It encompasses the glomerulus. It has an instinctive cell layer which has thickened membranes.Glomerulus is a narrow tuft which gets blood from the renal vessel. The blood is separated here by ultrafiltration into the bowman's capsule.The proximal convoluted tubule is the main site for the reabsorption of the water and salts into the circulatory system. It happens by uninvolved diffusion. The Loop of Henle is a U-formed cylinder having a descendent and ascendant appendages. The descending one is permeable to water while the ascending tube is porous to the ions. Distal Convoluted Tubule is the last site for reabsorption. To keep up with the blood osmolarity, the water is diffused. The antidiuretic chemical expands the penetrability of the tubule.
The nephron utilizes four mechanisms to change over blood into the urine. They are filtration, reabsorption, discharge, and excretion. The essential capacity of nephrons is to eliminate all byproducts from the blood. The blood passes by means of the glomerulus with high pressing factor, the little atoms are moved into the glomerular capsules. The cells present in each cylinder retain various particles barring the glucose, water, and others. It directs the liquid volume in our body.
Note:
Kidneys are responsible for making urine as concentrated as possible. This concentration is performed by the loop of Henle. The filtrate in the proximal convoluted tubule is isotonic to the renal blood flow. The nephron concentrates urine four times the renal blood concentration. Kidneys reabsorbs glucose, proteins etc.
