Question
Question: Describe the shapes of \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ & BH}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}\] ....
Describe the shapes of {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ & BH}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }} . Assign the hybridization of boron in these species.
Solution
Determine the number of bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons around the central atom in each compound. Based on the total number of lone pairs and bond pairs of electrons, assign the type of hybridization. From the type of hybridization, determine the geometry.
Complete answer:
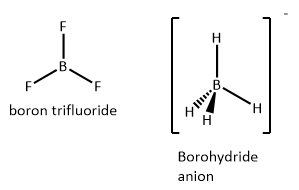
The atomic number of boron is 5. The electronic configuration of boron is 1s22s22p1 . A boron atom has three valence electrons. In the boron trifluoride molecule, the boron atom is the central atom with three boron-fluorine single bonds. The number of lone pairs of electrons on a boron atom is 0. Thus, the total number of lone pairs and bond pairs of electrons (the steric number) is three. Steric number of three is associated with sp2 hybridization. Boron atoms undergo sp2 hybridization. 2s,2px,2py atomic orbitals participate in hybridization to form three degenerate hybrid orbitals. These three hybrid orbitals of boron overlap with orbitals of three fluorine atoms to form three boron fluorine single bonds. The molecular shape is trigonal planar. Central boron atoms and three fluorine atoms are in a plane. Three fluorine atoms are present at three corners of a triangle. The Boron atom is present at the center of the triangle. The fluorine-boron-fluorine bond angle is 120∘.
In the borohydride anion, the boron atom is the central atom with four boron-hydrogen single bonds. The number of lone pairs of electrons on a boron atom is 0. Thus, the total number of lone pairs and bond pairs of electrons (the steric number) is four. Steric number of four is associated with sp3 hybridization. Boron atoms undergo sp3 hybridization. 2s,2px,2pz,2py atomic orbitals participate in hybridization to form four degenerate hybrid orbitals. These four hybrid orbitals of boron overlap with orbitals of four hydrogen atoms to form four boron hydrogen single bonds. The molecular shape is tetrahedral. Four hydrogen atoms are present at four corners of a regular tetrahedron. The Boron atom is present at the center of the tetrahedron. The hydrogen-boron-hydrogen bond angle is 109.28∘.
Note: Since in boron trifluoride molecule and borohydride anion, the number of lone pairs of electrons is zero, the molecular/ ionic geometry is the same as electron pair geometry. If the number of lone pairs of electrons is not equal to zero, then the molecular / ionic geometry will be different from electron pair geometry.
