Question
Question: Describe the events in the process of photosynthesis and give the chemical equation....
Describe the events in the process of photosynthesis and give the chemical equation.
Solution
Photosynthesis is the process of phototrophs converting light energy into chemical energy, which is then used to power cellular functions. Sugars are utilised to store chemical energy and are created from water and carbon dioxide.
Photosynthesis is defined as a process that occurs primarily in chloroplasts and is mediated by photosynthetic pigments such as chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotene, and xanthophyll. Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight to create nutrition in green plants and a few other autotrophic species. As a by-product of photosynthesis, oxygen is produced.
Complete answer:
During photosynthesis, there are three sets of events that occur. The following are the events that occur throughout the photosynthesis process:
The first event that occurs is the absorption of light energy in the form of sunshine by chlorophyll.
The conversion of light energy into chemical energy, which involves the breaking of water molecules, is the second step in the photosynthetic process. The water molecule is split into hydrogen and oxygen.
The conversion of carbon dioxide into carbohydrates is the third and last step in the photosynthetic process.
The stomata remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, while the release of oxygen is called waste product elimination.
Stomata play an important function in the photosynthesis process. Stomata are the pores via which gases are exchanged.
The chemical equation for the photosynthesis process:
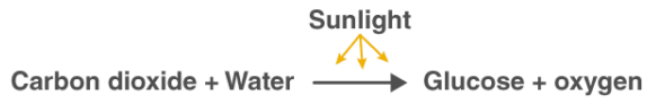
6CO2+ 6H2O→C6H12O6 + 6O2
Where,
CO2 is carbon dioxide
H2O is water
C6H12O6 is glucose
O2 is oxygen
Along with the above mentioned, light energy in the form of sunlight is also required
Note:
Factors affecting photosynthesis-
Light Intensity: As light intensity rises; the rate of photosynthesis rises as well. Low light intensity, on the other hand, leads to a slower rate of photosynthesis.
The CO2 concentration is as follows: The rate of photosynthesis is aided by a higher carbon dioxide concentration. Carbon dioxide in the range of 300−400 PPM is usually sufficient for photosynthesis.
Temperature: A temperature range of 25∘−35∘ C is required for efficient photosynthesis to take place.
Water: Because water is such a vital component of photosynthesis, a lack of it might cause problems with carbon dioxide absorption. Due to a lack of water, stomatal openings refuse to keep the amount of water they have stored inside.
Industrial chemicals and other particulates may land on the leaf surface, causing pollution. This can clog stomatal pores, making it difficult to absorb carbon dioxide.
