Question
Question: Describe schematically the equipotential surfaces corresponding to (A) A constant electric field i...
Describe schematically the equipotential surfaces corresponding to
(A) A constant electric field in z-direction
(B) A field that uniformly increases in magnitude but remains in a constant (say, z) direction
(C) A single positive charge at the origin
(D) A uniform grid consisting of long equally spaced parallel charged wires in a plane.
Solution
Hint : Here, we have to describe each point given in the options above and give a proper representation of electric field lines and equipotential surfaces corresponding to each of them. We have to understand that the electric field lines are always perpendicular to the equipotential surfaces.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us consider E as the electric field vector and r be the direction.
A constant electric field in z-direction means the magnitude of electric field and the direction both are same, for better understanding let us see the figure below:
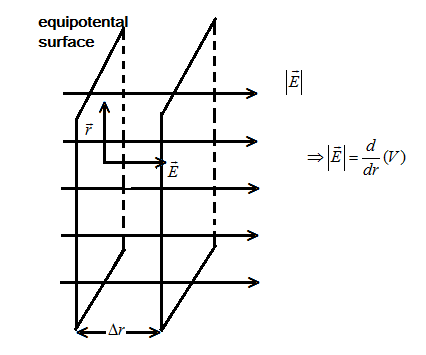
Here, E⊥r , r is along the surface of the equipotential surface, as shown in the figure above. Also the magnitude of electric field is given as E=drd(V) ; V is the potential , Δr is the distance between two equipotential surfaces.
A field that uniformly increases in magnitude but remains in a constant (say, z) direction
To understand this, we will consider the figure below:
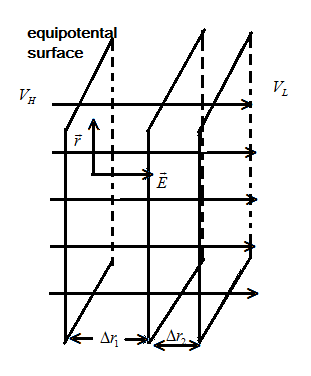
In this figure, the electric field line is in the same direction but varying in magnitude, so when there is an increase in magnitude of electric field then there is an increase in potential difference too.
Also, as we move from left to right the potential decreases from high to low as shown in figure. The distance between the equipotential surfaces also decreases, which means the surfaces are coming closer to each other ( Δr2<Δr1 ) and the E⊥r remains the same.
A single positive charge at the origin
Let us consider a charge at the origin and represent it in the figure below:
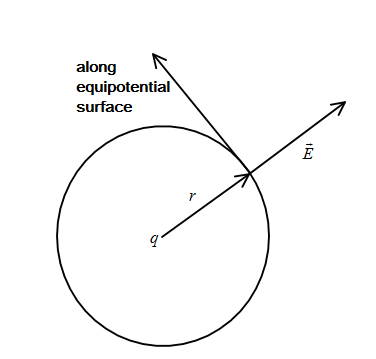
Here, the circular surface surrounding the +q charge acts like an equipotential surface and the direction will be tangential to the surface. An electric field vector is radially outwards from the equipotential surface as shown in figure.
A uniform grid consisting of long equally spaced parallel charged wires in a plane.
Let us represent the grid with the help of the diagram given below:
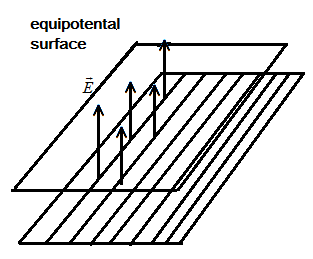
Thus, here we see that the equipotential surface is exactly parallel to the grid of wires in a plane. The electric field vector is outwards above the plane and perpendicular to the vector along the surface of the equipotential surface.
Note :
Here, we have described the schematically the equipotential surfaces corresponding to the points given in A, B, C and D in a very descriptive manner. An equipotential surface is that at every point of which potential is the same and it is described by the given example above.
