Question
Question: Describe briefly with the help of a circuit diagram, how the flow of current carriers in a p-n-p tra...
Describe briefly with the help of a circuit diagram, how the flow of current carriers in a p-n-p transistor is regulated with emitter-base junction forward biased and base-collector junction reverse biased.
Solution
A PNP transistor is a bipolar junction transistor built between two semiconductors of the P-type by sandwiching an N-type semiconductor. A PNP transistor has three terminals: Collector (C), Emitter (E) and Base (B). The PNP transistor works like two PN junction diodes attached back to back.
Complete step by step answer:
-PNP functions in the same, but opposite, manner. The foundation also governs the current flow, but the current flows from the emitter to the collector in the opposite direction. The emitter releases "holes" (a hypothetical loss of electrons) that are captured by the collector instead of electrons.
Forward bias: The junction of the emitter base is forward biased, meaning that the p type emitter is attached to the battery's positive pole and the n type base is connected to the negative pole of the same VEE battery.
Reverse bias: The reverse biased collector base junction indicates that the n type base is attached to the positive battery pole and the p type emitter is attached to the negative pole of the same battery VCC.
-VEE is forward biased at the emitter base junction and VCC is reverse biased at the collector base junction. The holes in the emitter are driven into the foundation by the positive voltage VEE battery terminal. It is thin and mildly doped at the surface. Therefore, only a few holes in the base merge with electrons. Base current IB is therefore small. Almost 99% of the holes coming from the emitter are captured by the collector since VCC is huge.A bond breaks in the emitter and electron which enters the positive terminal of the emitter-base battery are released with each hole consumed in the collector.
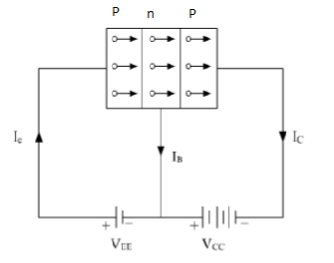
Note: The current in the transistor p-n-p is due to holes, but the concentration is retained at all time; the current in the external circuit is due to electron flow.
