Question
Question: Describe a method for the identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Also write chemi...
Describe a method for the identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Also write chemical equations of the reactions involved.
Solution
Hint: To answer this question we have to recall the difference between the three amines. We should also remember the Hinsberg test which differentiates between the three.
Complete step by step solution:
Aliphatic amines occur in nature, principally as products of the protein material, but they are also present in living tissue. Amines are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary according to the number of carbons bonded directly to the nitrogen atom. Primary amines have one carbon bonded to the nitrogen. Secondary amines have two carbons bonded to the nitrogen, and tertiary amines have three carbons bonded to the nitrogen
Primary, secondary and tertiary amines react differently with Hinsberg reagent (Benzosulphonyl chloride) in presence of an aqueous alkali. Hence, we generally use the Hinsberg test to distinguish between amines.
- Primary amine reacts with Hinsberg reagent to form a N-alkylbenzenesulphonyl amide which is observed to be soluble in the aqueous alkali.
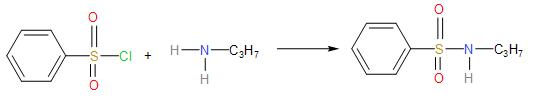
Since, there is a strong electron withdrawing group in the sulphonamide; the hydrogen atom attached to the nitrogen is easily released as proton. Hence, it dissolves the alkali.
- But, we see that secondary amines react with Hinsberg reagent to produce a sulphonamide which remains insoluble in the alkali.
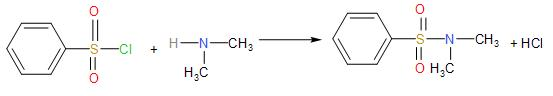
Since, there is no hydrogen atom attached to the nitrogen atom of sulphonamide, it does not dissolve in the alkali.
- In contrast to these Tertiary amines do not react with Hinsberg reagent at all.
Note: We can use another method to distinguish between amines. This is known as the Hoffman method. Primary amine yields a solid product with ethyl oxalate, secondary amine yields a liquid product whereas no reaction takes place in case of tertiary amines.
