Question
Question: Define torque. Show that torque acting a particle is the product of force and the lever arm about th...
Define torque. Show that torque acting a particle is the product of force and the lever arm about the centre of rotation.
Solution
Torque is the rotational equivalent of force which produces rotating effect. It is also known as moment or moment of force. Its effect depends on the point of application of force.
Complete step by step answer:
Torque is the rotational analogue of force and expresses the tendency of a force applied to an object to cause the object to rotate about a given point. In simple words, torque produces the same effect in rotation motion that force produces in linear motion.
Let’s prove that torque acting on a particle is the product of force and the lever arm about the centre of rotation by discussing an experiment.
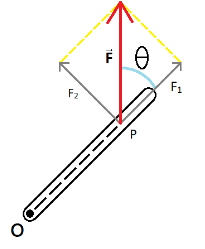
Consider a rod pivoted at the point O. A force F is applied on it at the point P. The component Fcosθ of the force along the rod is counterbalanced by the reaction force of the pivot and cannot contribute to the rod. It is the component Fsinθ of the force perpendicular to the rod, which is responsible for rotation of the rod. Moreover, farther is the point P from O, where the force is applied easier is to rotate the rod. This is why the handle on a door is attached as far away as possible from the hinges. Here F2=Fsinθ and F1=Fcosθ
Magnitude of torque of a force is proportional to the product of distance of point of application of the force from the pivot and magnitude of the perpendicular component Fsinθ of the force. Denoting torque by symbol τ, the distance of point O application of force from the pivot by r, we can write τo∝rFsinθ.
Since rotation has a sense of direction, torque should also be a vector. Its direction is given by right hand rule. We can now express torque by the cross product of r andF.
⇒τo=r×F
Here constant of proportionality has been assumed a dimensionless number unity because a unit of torque has been chosen as a product of unit of force and unit of length.
The geometrical construction shown in figure suggests a simple way to calculate torque. The line OQ=rsinθ, known as moment arm, is the length of perpendicular drawn from O on the line of action of the force. The magnitude of the force equals the product of OQ and magnitude of the force F.
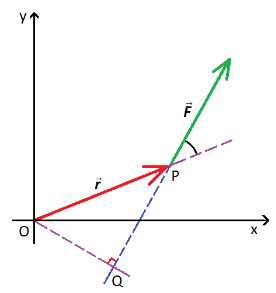
Hence torque of force F about a point O is τo=r×F. For a body to be in rotational equilibrium τnet=0 i.e., If a body is under the action of several external forces F1,F2,F3,......,Fn. Then for the body to be in Rotational equilibrium ∑τP=0.
Note: An object can be in Translational equilibrium but can’t be in rotational equilibrium at the same time. Example: Force couple. Practical significance of torque can be observed in day-to-day life when opening the door, we feel more ease in opening the door when we push the door farther than the hinge as compared to near the hinge.
