Question
Question: Define the following term: Zeta potential....
Define the following term:
Zeta potential.
Solution
Zeta potential is also known as Electrokinetic. It is used to define or explain the process of preferential adsorption of ions from solution in the electrical charge on colloidal particles. There are two layers: the fixed layer and the diffused layer.
Complete step by step answer:
The stability of the colloidal sol is defined by some properties. The electrical charge on the colloidal particle is one of them. The electrical charge on the colloidal particle is explained by the process of preferential adsorption of ions from the solution. During the preparation of colloidal sol, an ionic colloidal adsorb ions common to its lattice.
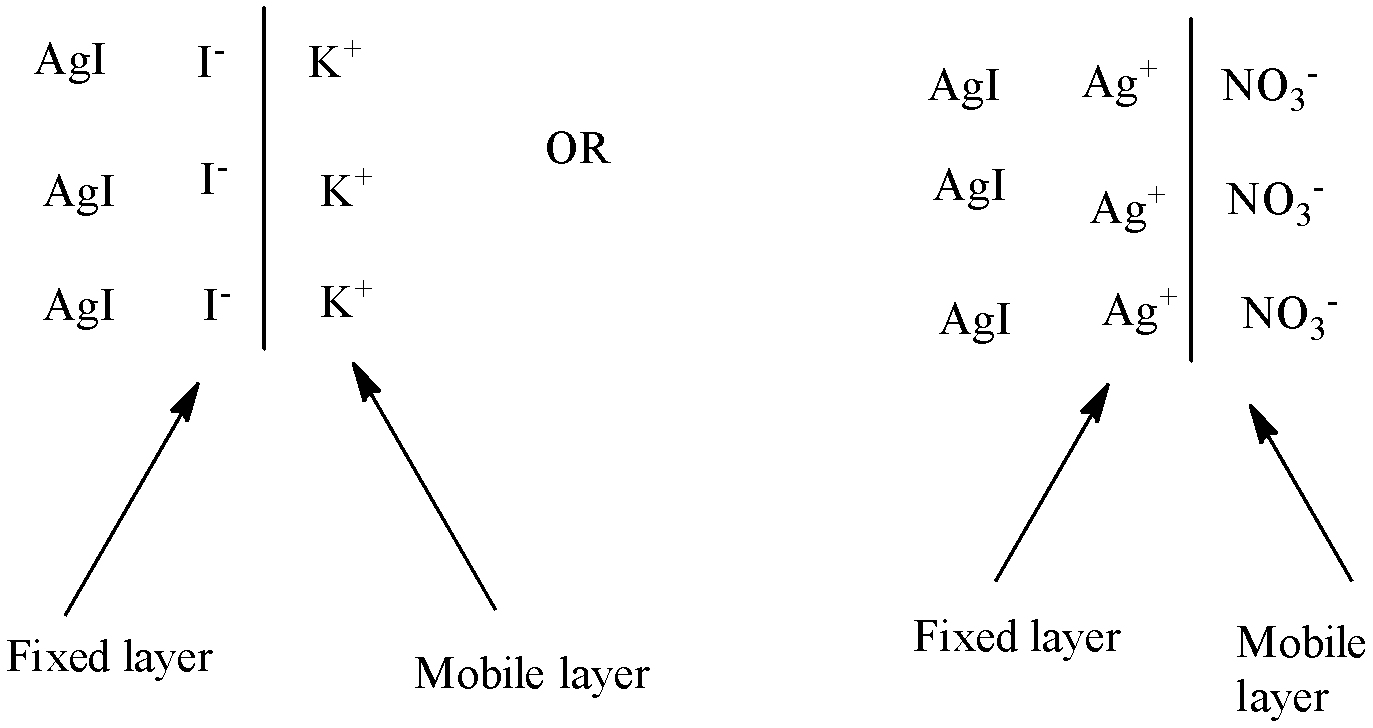
It can be explained by the colloidal sol AgI is prepared by adding KI solution to the AgNO3 solution till KI is in slight excess, iodide ion (I−) will be absorbed in the surface of AgI particles thereby giving them a negative charge:
AgI+I−→AgI:I−
The same can be done if the colloidal sol AgI is prepared by adding AgNO3 solution to the KI solution till AgNO3 is in slight excess, iodide ion (Ag+ ) will be absorbed in the surface of AgI particles thereby giving them a positive charge:
AgI+Ag+→AgI:Ag+
This can be explained when one type of ions of the electrolyte is adsorbed on the surface of the colloidal particles, there is a formation of a 'fixed layer'. This layer attracts the counter ions from the medium forming a mobile layer known as 'diffused layer'. This potential difference is known as electrokinetic or zeta potential.
Note: Helmholtz electrical double layer is the double layer of opposite charge formed in the zeta potential layer. So, the left-out excess ions remain in the solution thereby giving equal and opposite charge to the dispersion medium.
