Question
Question: Define photophosphorylation and describe cyclic phosphorylation....
Define photophosphorylation and describe cyclic phosphorylation.
Solution
In the word, photophosphorylation - Photo means light and phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphoryl group to a molecule. Cyclic phosphorylation is termed due to the movement of electrons in a cyclic manner.
Complete answer:
As understood from the etymology, photophosphorylation is a process in which plants convert adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through phosphorylation using sunlight as an energy source. The ATP produced is the source for energy for the cells. This phosphorylation is of two types: cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Cyclic photophosphorylation, occurring on the stroma lamellae or fret channels, is initiated by the high-energy electron produced by chlorophyll A in p700 of photosystem 1 (PS 1) through sunlight. The electron produced activates a series of events starting from the primary acceptor to ferredoxin to plastoquinone then to cytochrome b6f to plastocyanin and finally goes back to PS 1. During this excitation, two ATP molecules are released. The proton motive force generates a concentration gradient which can be used during chemiosmosis.
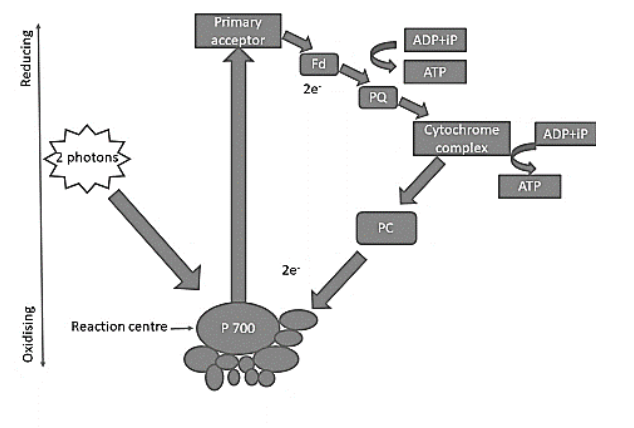
Note: Cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation are entirely different. In cyclic photophosphorylation, only PS 1 is involved whereas in non-cyclic both PS 1 and PS 2 are involved. Neither oxygen nor NADPH is released during cyclic photophosphorylation but both are released during non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Similarly, cyclic photophosphorylation also occurs in photosynthetic bacteria to meet their energy needs. Bacteria have only one photosystem 1 whose chlorophyll absorbs wavelengths of 800−1000nm, unlike plants which absorb 650−750nm. However, cyanobacteria possesses two photosystems and performs similar to plants. In plants H2O donates electrons to photophosphorylation. But in bacteria H2Sand other chemical compounds donate electrons to generate energy.
