Question
Question: Define and design a test cross....
Define and design a test cross.
Solution
Test cross is introduced by Gregor Johann Mendel and it’s performed to determine the genotype of the phenotypically dominant plant. The dominant traits in diploid organisms can be due to homozygous or heterozygous genotypes.
Complete answer:
Test cross is defined as the cross between a phenotypically dominant and a recessive plant in order to determine the genotype of the dominant plant. This is done by analysing the progeny of the next generation. Diploid organisms exhibit dominant traits because of homozygous or heterozygous conditions.
Homozygous refers to the condition where both the alleles for a single gene are of the same type. Whereas, heterozygous refers to the condition where the two alleles for a single gene are of different types. For example, Seed color in garden pea plants, yellow (Y) is the dominant trait, and green (y) is a recessive trait. YY and yy represent the homozygosity and Yy represents the heterozygosity.
When the plant of dominant phenotype, whose genotype is to be determined is crossed with a recessive one, the progenies are analysed in order to determine the genotype of the dominant parent. If a plant with yellow coloured seed, possessing genotype of YY is crossed with a plant with green coloured seed (yy), all the progenies produce yellow coloured seed (Yy). On the other hand, when a plant with yellow coloured seed, possessing genotype of Yy is crossed with a plant with green coloured seed (yy), half of the progenies produce yellow seeds (Yy) and the other half produces green seeds (yy).
Hence, when the dominant parent is homozygous in nature, all the progenies produce a dominant trait. And, when the dominant parent is heterozygous in nature, there is an equal ratio of progenies with a dominant and recessive trait.
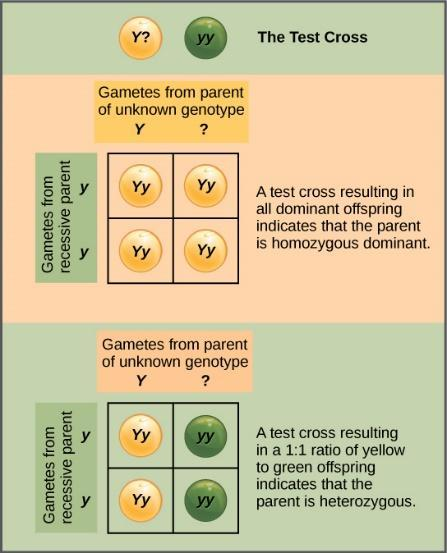
Note: It is significant to know the significance of the test cross. It is performed mainly to determine the genotype of the dominant parent, by analyzing the progeny of the next generation. If all the progenies are dominant, the parent is homozygous dominant and if progenies possess an equal ratio of a dominant and recessive trait, the parent is heterozygous dominant.
