Question
Question: Decreasing order of heat of hydrogenation? I.
II.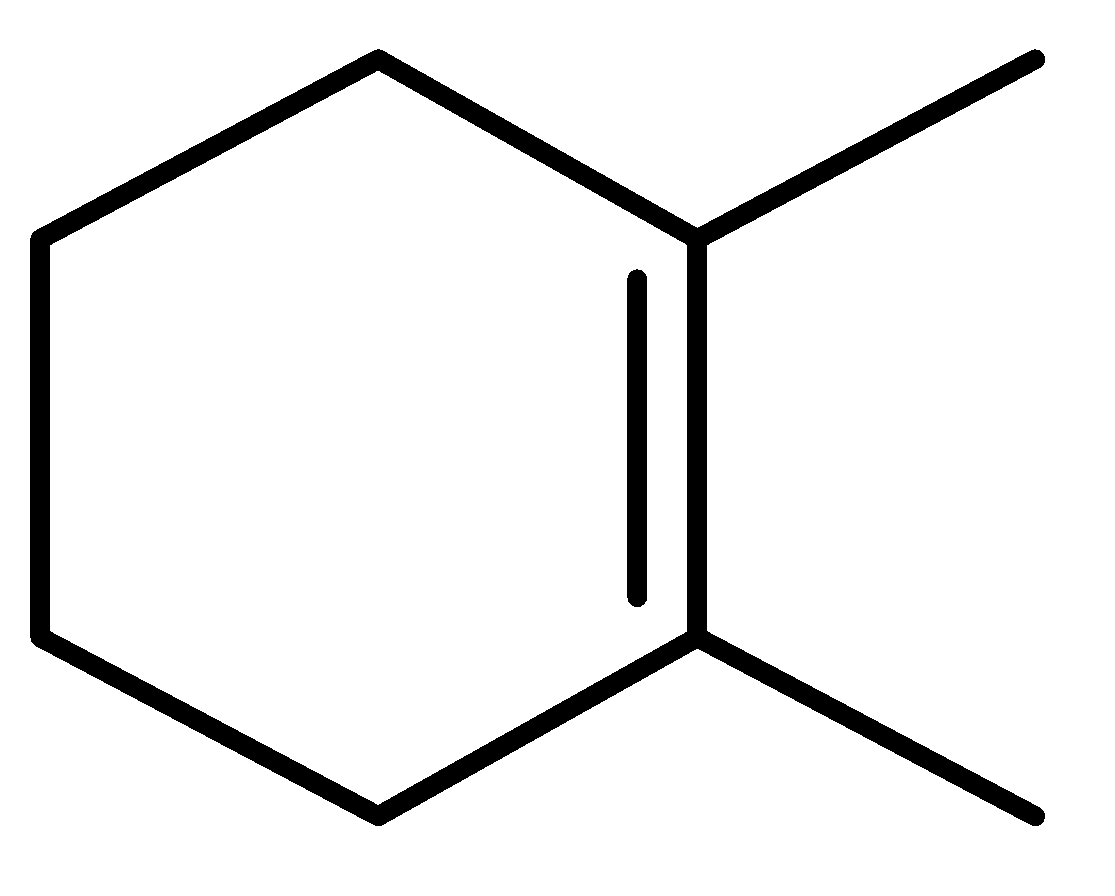
III.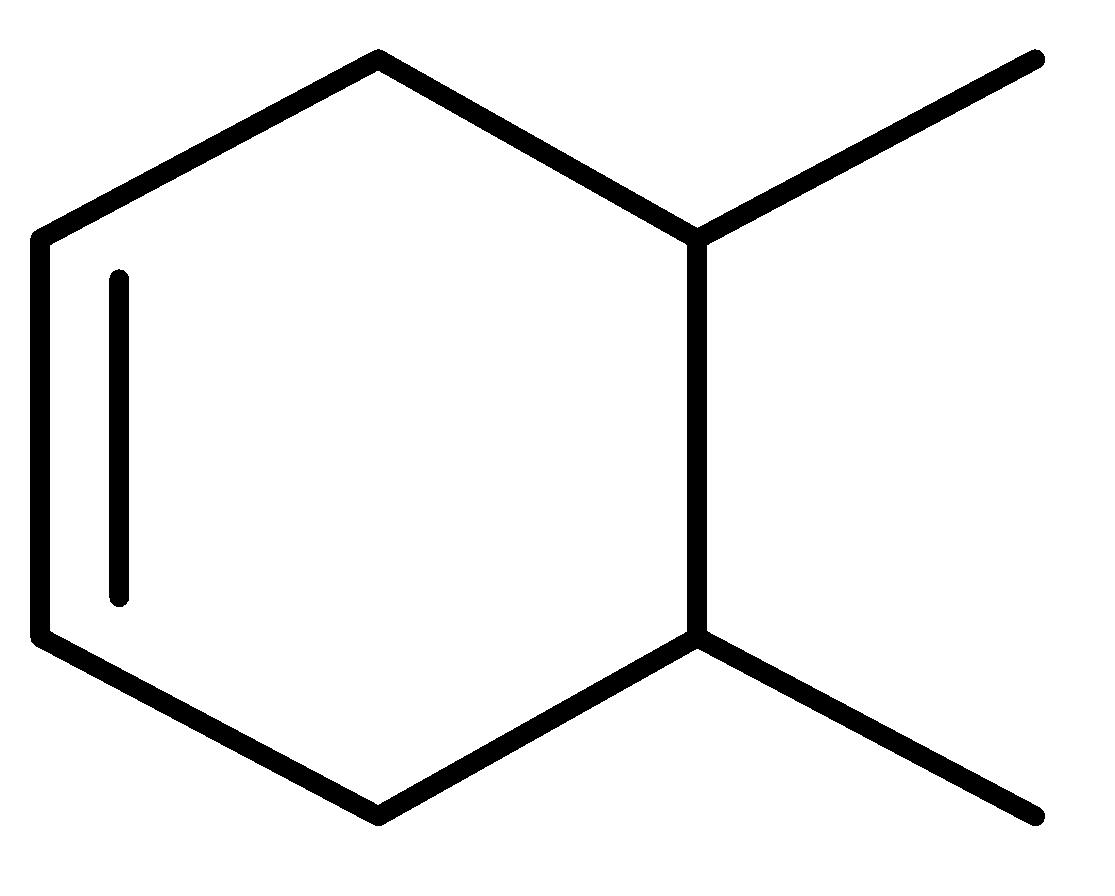
A.I>III>II
B.II>I>III
C.III>I>II
D.II>III>I
Solution
There are three cyclic compounds given and a double attached to it. We have to find the order of heat of hydration. Heat of hydration can be predicted by looking at the stability of the compounds. Heat of hydration is the standard enthalpy of hydrogenation of an alkene. The catalytic hydrogenation of an alkene is an exothermic process. So, this indicates that the heat of hydrogenation of alkene is always negative.
Complete answer:
Heat of hydration is defined as the amount of energy released when one mole of ions undergo hydration. It is also termed as hydration enthalpy. It is the standard enthalpy of catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes. The heat of hydrogenation depends on the stability of alkenes. Stability of alkenes indicates that they do not convert into alkanes. If an alkene is stable or not, it is predicted by the hyperconjugation effect. Hyperconjugation depends on the number of alpha- hydrogens.
The carbon to which double bond is attached is called alpha- carbons and its hydrogen is called alpha hydrogen. If the number of alpha hydrogens are more, the stability of alkenes increases.
If the stability of alkenes is more, then heat of hydration is less and if the stability of alkenes is less then the heat of hydration is more.
In the given question, three compounds are given and their stability order will be:
Order of stability: II>III>I
So, the heat of hydration is the reverse of the stability order.
Decreasing order of heat of hydrogenation-I>III>II
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note:
Stability of alkenes is the important factor to determine the heat of hydrogenation. The stability of alkenes depends on hyperconjugation and steric hindrance. The molecules will be less stable if the steric hindrance of molecules is high.
