Question
Question: Correct statement(s) in case of n-butanol and t-butanol is (are): A. both are having equal solubil...
Correct statement(s) in case of n-butanol and t-butanol is (are):
A. both are having equal solubility in water.
B. t-butanol is more soluble in water than n-butanol.
C. The boiling point of t-butanol is lower than n-butanol.
D. boiling point of n-butanol is lower than t-butanol.
Solution
For the above problem, you can basically look up the dependence of boiling point and solubility on branching. More branching results in high solubility. This is because as branching increases, the surface area of the nonpolar hydrocarbon part decreases that results in increased solubility. Further, More branching means less will be the boiling point.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, we will look at the chemical formulas of n-butanol and t-butanol.
N-butanol is a straight chain compound whereas t-butanol involves branching.
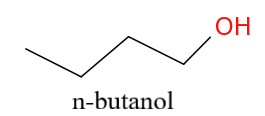
This is n-butanol i.e. C4H9OH.
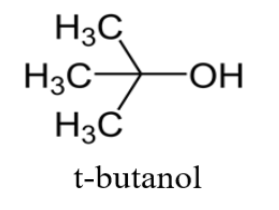
This is t-butanol or what we call as tertiary butanol.
As it is clear, from the chemical formulas t-butanol involves branching while n-butanol is a straight chain compound.
Boiling point depends upon branching. More branching means less will be the boiling point. That is, boiling point is inversely proportional to branching.
So, in the above two cases the boiling point of t-butanol will be lower as compared to n-butanol.
Now, comes to solubility. Solubility extent of alcohols in water actually depends on the ability of the molecule to form hydrogen bonds with water. As molecular mass increases, the alkyl group (hydrocarbon part) becomes larger which causes resistance in the formation of the hydrogen bonds with water and as a result the solubility decreases. Solubility depends on the alkyl group part that means larger the alkyl group, lesser the solubility. But in case of isomeric alcohols, solubility depends on branching. This due to the fact that as branching increases the surface area of non-polar hydrocarbon part decreases that results in increased solubility.
So, t-butanol will be more soluble than n-butanol in regard with the above concept.
Hence option B and C are correct.
Note:
Do not confuse between dependence of solubility and boiling point on branching. Key point to keep in mind is that solubility is directly proportional to branching whereas boiling point is inversely proportional to branching.
