Question
Question: Coordination number of \[{\text{Cr}}\] is six. A complex with \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}_{\...
Coordination number of Cr is six. A complex with C2O42 - , en and superoxide O2 - will be in the ratio to make complex [Cr(C2O4)x(en)y(O2)z] -
1. x = 1, y = 1, z = 1
2. x = 1, y = 1, z = 2
3. x = 1, y = 2, z = 2
4. x = 2, y = 1, z = 1
Solution
The coordination number of chromium is six, hence it is in + 3 oxidation state. It can form a coordinate bond through six donor ligand atoms. Therefore, the denticity of each ligand given should be known.
Complete step by step answer:
The given coordination compounds are as follows.
[Cr(C2O4)x(en)y(O2)z] -
In this compound we have to find the x,y and z values.
The central metal atom – Chromium.
Chromium atomic number – 24
Electronic configuration -[Ar]3d44s2. And it is 3d44s2system. Hence, it has a total six valence electrons available for the formation of coordinate bonds.
For x value:
The ligand oxalate (C2O42 - ) is a bi-dendate ligand means which donate two pairs of electrons to a central metal atom.
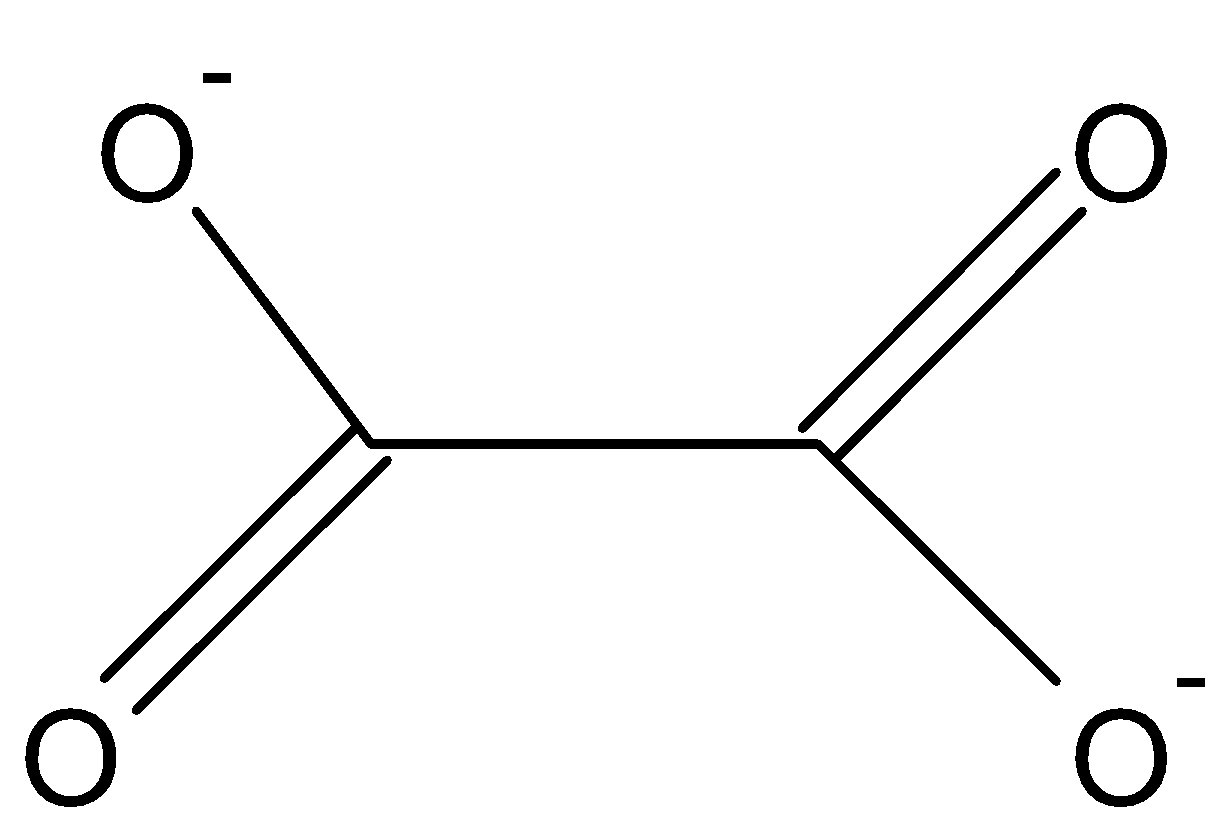
Figure 1: Oxalate ion
Hence, the coordination number is 2.
For y value:
The ligand ethylenediamine (en) is also bi-dendate ligand and it is a neutral ligand.
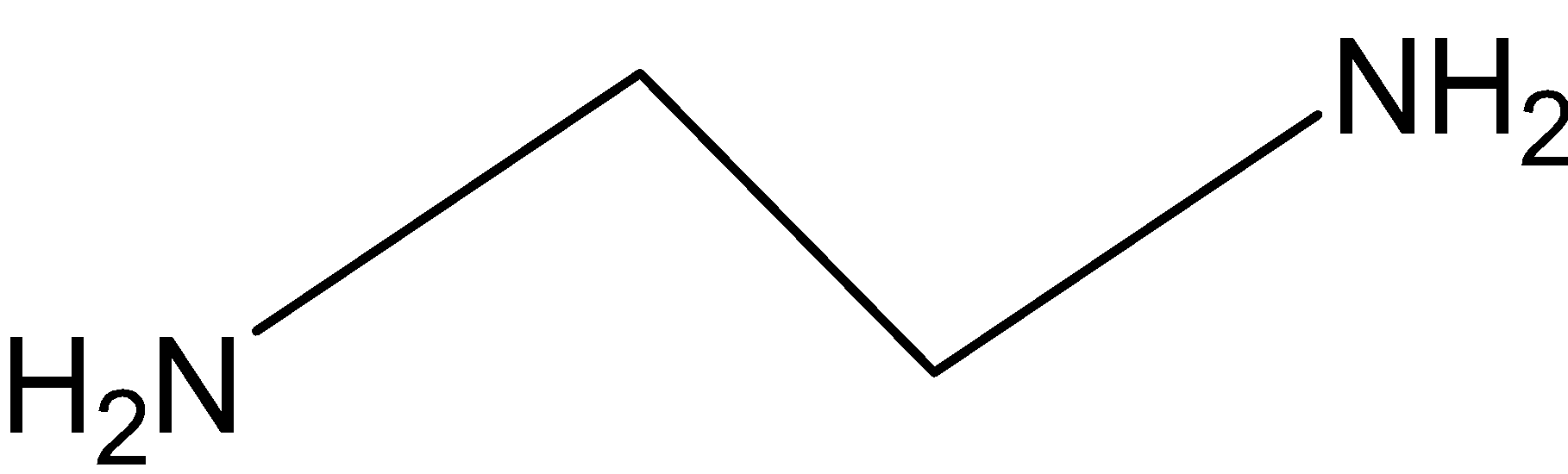
Figure 2: Ethylene diamine
Hence, the coordination number is 2.
For z value
The ligand superoxide (O2 - ) is a mono-dendate ligand. Hence, the coordination number is 1.
Since, the coordination number central metal atom is 6. All these x, y and z values are equal to the 6.
2x + 2y + z = 6………………………(1)
From Charge-balance equation:
[Cr(C2O4)x(en)y(O2)z] -
The Croxidation state + 3, Oxalate ion (C2O42 - ) oxidation state is - 2 , ethylenediamine oxidation number is zero and superoxide ion oxidation number is - 1.
3×1+(−2)×x+0×y+(−1)×z=−1
- 2x - z = - 4
2x + z = 4………………………………..(2)
Substitute this value in equation (1)
4 + 2y = 6
y = 1
Now, since, x,y and z represent the number of ligands. Hence, it has an integral value and it cannot be zero.
Therefore, x = 1.
x = 1 and y = 1
Substitute these values in equation (1)
Therefore, x = 1,y = 1 and z = 2.
Hence, the correct option is 2.
Additional information:
-A coordination compound is basically a neutral species consisting of an uncoordinated ion and coordinated complexes to maintain the overall charge balance of a complex.
-In these compounds [ ] are mainly used to indicate the atomic composition of those are atoms and the ligands.
-Species which are present in the outside of [ ] are not coordinated to the central metal atom but these maintain overall charge of a complex.
Note:
Denticity of the ligand is the number of pairs of electrons shared with the metal atom. The poly-dendate ligands form the ring structure with the metal ion and hence contribute to extra stability. This is known as chelate effect.
