Question
Question: Consider the graph given in figure. When of the following options does not show instantaneous rate o...
Consider the graph given in figure. When of the following options does not show instantaneous rate of reaction at 40s:
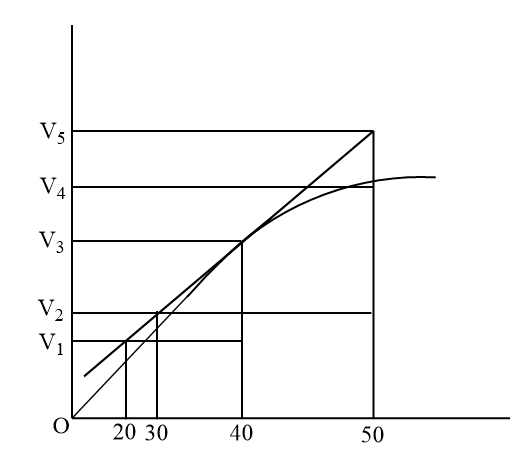
(A) 50−30V5−V2
(B) 50−30V4−V2
(C) 40−30V3−V2
(D) 40−20V3−V1
Solution
The rate of those reactions which occur at a specific time period of a very short interval is referred to as instantaneous rate. We can find the value of instantaneous rate with the help of plotting rate vs. time graph.
Complete answer:
The rate of chemical reaction which occurs at some instant at a particular time is known as the instantaneous rate. It can also be defined as change in the concentration of the compounds of a reaction at a very small time interval. The mean of the rate of instantaneous reaction over the period of the time gives the mean rate while the reaction.
To determine the rate of instantaneous reaction we will need to plot the graph of the change in the rate of the reaction along the x-axis and the time interval along the y-axis. By using the graph we are able to calculate the negative of the slope of the curve of the change in concentration of the reactant with respect to the time t . This can be done by measuring the slope of the tangent to the graph of the concentration vs. time.
By using the given graph which is:
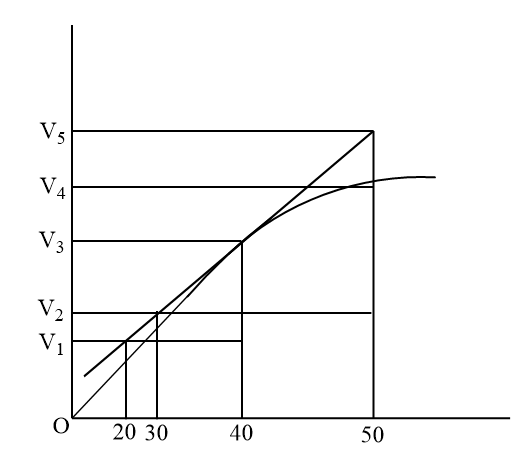
In this graph tangent is already drawn and also extends the endpoints of the tangent along the x and y axis. Thus triangles are formed which is convenient for the calculation of the value of the change in the concentration of the product P with time i.e.
Instantaneous Rate=ΔtΔP
Where, ΔP is the change in concentration and Δt is the change in time.
Now according to the question, option (b) is not correct as in the graph we can see that the instantaneous at this point duration in the straight line slope gives inexact data. Thus the answer to this question is option (b) .
Note:
As we can see that the concentration rate of the product depends upon time it increases with time and also the rate of concentration of reactants decreases with time. Thus we get a negative slope when there is a change in the concentration of reactant with time.
