Question
Question: Consider the following statements each with two blanks. (i) Diaphragm contracts to help in ___(1)__ ...
Consider the following statements each with two blanks. (i) Diaphragm contracts to help in _(1) while the contraction of abdominal muscles helps in (2).
Solution
The diaphragm is present behind the lungs and is the main respiratory muscle. It helps in taking in the air and releasing the air out.
Diaphragm contracts to assist in (1) inspiration while abdominal muscle contraction aids in (2) forced expiration.
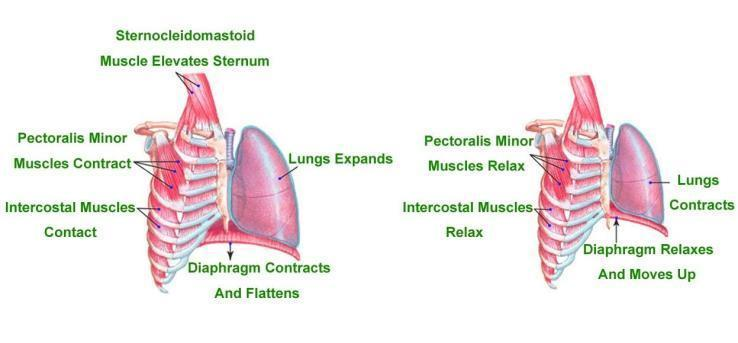
The diaphragm is situated beneath the lungs and is the main respiratory muscle. It is a big, dome-shaped muscle, which involuntarily contracts rhythmically and continuously. The diaphragm contracts and flattens when inhaled and the chest cavity widens. The contraction produces a vacuum and forces air into the lungs. The diaphragm relaxes after exhalation and returns to the dome shape.
The diaphragm muscles originate from the lower part of the sternum (breastbone), the lower six ribs, and the spine's lumbar (far) vertebrae, and are connected to a central membranous tendon. The diaphragm contraction raises the internal height of the thoracic cavity, thereby reducing its internal pressure and inducing air inspiration.
Relaxation of the diaphragm and the inherent elasticity of the lung tissue and the thoracic cage produces expiration. Also, the diaphragm plays an important role in expulsive acts such as coughing, sneezing, vomiting, crying, and expelling blood, urine, and the fetus, in parturition (childbirth). The diaphragm is perforated by several structures, especially the esophagus, aorta, and lower vena cava, and is often subjected to a herniation (rupture). Small holes in the membranous portion of the diaphragm often cause irregular fluid or air accumulations to travel from the abdominal cavity (where pressure during inspiration is positive) into the pleural spaces of the chest (where pressure during inspiration is negative). The diaphragm's intermittent inspiratory motion produces the signature sound during hiccupping.
Note:
The diaphragm is a muscle of respiration that is activated on inhalation. We cannot actively regulate its behavior but when it is triggered, we may become aware of how it feels. Diaphragm breathing is essential for effective and deep singing. We may experience one or more of the following symptoms, depending on the cause of your diaphragm pain: discomfort and shortness of breath after eating. A "stitch" to the hand while exercising, the inability to breathe to the full are the symptoms of diaphragm pain.
