Question
Question: Consider the following reaction sequence: \(\text{ Metal (M) }\xrightarrow{\text{Very dil}\text{.H...
Consider the following reaction sequence:
Metal (M) Very dil.HNO3 no reaction
Metal (M) Conc.HNO3 light blue solution (A) + gas(B)
The incorrect statement(s) is (are):
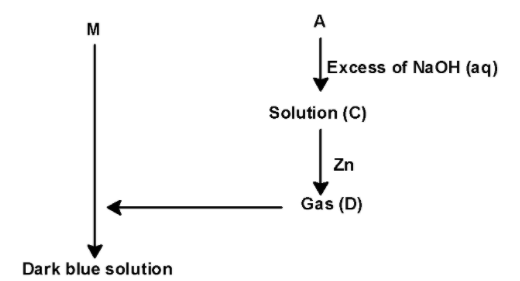
A) Gas (B) is diamagnetic.
B) Solution (C) contains the only NaNO2 salt
C) Dark blue solution is paramagnetic
D) Metal (M) is extracted by the thermite process
Solution
nitric acid is an oxidizing agent. It oxidizes the metal M to Mn+ . The nitric acid abstract the n electrons from the metal and reduced itself into the NOx gas and metal its nitrate salt. The metal can undergo the coordination complex interaction with the water. This gives a colour solution. Excess of sodium hydroxide in the solution forms a mixture of salts of nitrite and nitrate.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given the following reaction. Metal M does not react with dilute nitric acid HNO3 .the general reaction is as represented below,
Metal (M) Very dil.HNO3 no reaction
The metal reacts with the concentrated nitric acid and forms a blue coloured solution A with the liberation of gas B. The reaction is written as follows,
Metal (M) Conc.HNO3 light blue solution (A) + gas(B)
Nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent. It is used in a redox reaction.
Copper reacts with a concentrated nitric acid. Nitric acid itself accepts the electron and undergoes the reduction. Copper loses its two electrons and becomes Cu2+ .the oxidation reaction of copper is as shown below,
Cu → Cu2+ + 2e−
The nitric acid accepts these two electrons and forms a nitrate ion. The reduction reaction of nitric acid is as shown below,
4HNO3 + 2e− → 2NO3− + 2H2O
The reaction of copper with the concentrated nitric acid is as shown below,
4HNO3 + Cu → Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O
The speed of the reaction depends on the surface area of copper.
The solution changes the colour because it is an aqueous solution. The copper ion undergoes the coordination of complex interactions with the surrounding water molecules. This cording complex with the water is blue in colour.
This nitrogen dioxide NO2 is paramagnetic in nature. The nitrogen has an unpaired electron which makes it paramagnetic. Copper cannot be extracted through the thermite process. When copper nitrate solution is treated with sodium hydroxide NaOH , the copper hydroxide is formed as the product. The reaction of Cu(NO3)2 with NaOH as shown below,
Cu(NO3)2 + 2NaOH → Cu(OH)2 + 2NaNO3
The solution also contains NaNO2 .solution Cis a mixture of NaNO3 + NaNO2 . This solution C when treated with ammonia liberates ammonia gas.
Thus, in the given reaction
Metal (M) is Cu ,
Blue solution (A) is Cu(NO3)2 ,
Gas (B) is NO2 . It is paramagnetic.
Solution C is NaNO3 + NaNO2
Gas (D) is NH3
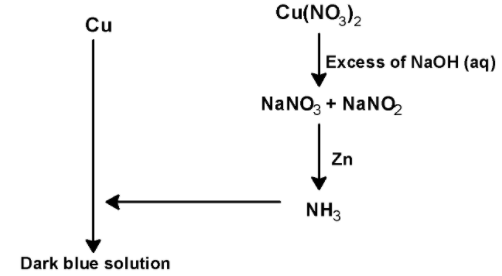
Thus, statement (C) correctly is valid.
Hence, (A), (B) and (D) are correct options.
Note: Dilute nitric acid reacts with the copper. However, the reaction for nitrogen oxide is the by -product. The nitric acid and oxidizing agent thus favours the reaction. Mineral acid like hydrochloric acid does not oxidize the copper, but sulphuric acid is a strong oxidizing agent and reacts with copper to release sulphur dioxide as a gas.
