Question
Question: Consider the following reaction: \(RCHO + N{H_2}N{H_2} \to RCH = N - N{H_2}\) What sort of reac...
Consider the following reaction:
RCHO+NH2NH2→RCH=N−NH2
What sort of reaction is this?
A) Free radical addition-elimination reaction
B) Electrophilic substitution-elimination reaction
C) Nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction
D) Electrophilic addition-elimination reaction
Solution
You must know that in a carbon-oxygen bond, the carbon centre is electrophilic while oxygen centre is nucleophilic in nature. Nitrogen contains lone pairs, so hydrazine (NH2NH2) in the given reaction will act as a nucleophile. It will attack the carbon centre of given aldehyde.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given the following chemical reaction:
RCHO+NH2NH2→RCH=N−NH2
We can represent the above given reaction with mechanism as:
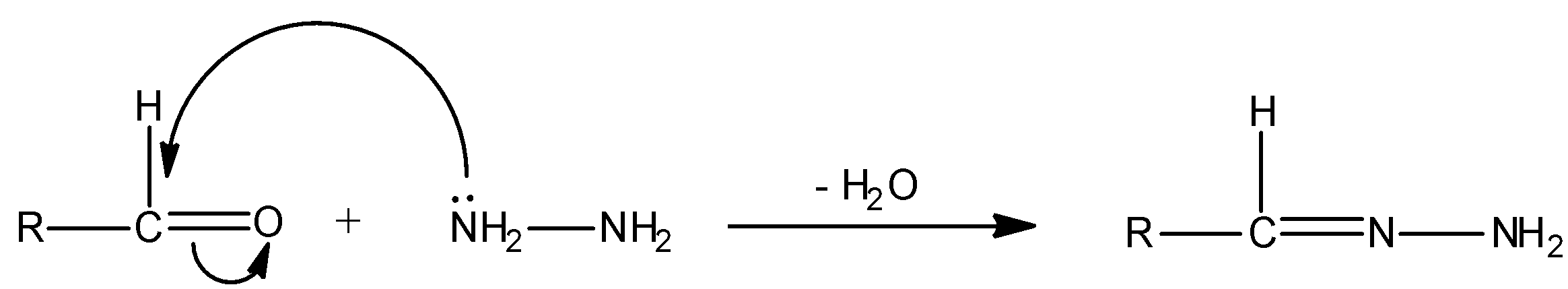
We all know that oxygen is more electronegative than carbon. So in a carbonyl bond i.e., carbon-oxygen bond, carbon is electron deficient always and oxygen is electron rich in nature. Thus, the carbon centre behaves as an electrophile. Here, hydrazine molecules (NH2NH2) are nucleophiles. This is because in hydrazine, nitrogen atoms contain lone pairs and hence it is electron rich or nucleophile. And, a nucleophile always attacks an electrophile. Hence, hydrazine molecules will attack the carbon centre (i.e., electrophile) of aldehyde (RCHO). When a nucleophile attacks on an electrophile, the reaction is termed as nucleophilic addition. So, when a molecule of hydrazine is added to the carbonyl group, this is the case of nucleophilic-addition reaction. Simultaneously, a water molecule is also eliminated in the given reaction. Thus, this is the case of elimination reaction. Hence, overall the given reaction is nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction.
Thus, option C is the correct answer.
Note: Aldehydes or ketones react with hydrazine to give hydrazones (hydrazine derivative) and further, hydrazones can be converted to corresponding alkanes by reaction with base and heat. These two steps can be converted into one reaction known as Wolff-Kishner reduction. In the first step, a water molecule is eliminated and in the second step, nitrogen gas is produced as the by-product in the reaction.
