Question
Question: Consider the above reaction in which compound (A) on reaction with \[EAA\left( MeCOC{{H}_{2}}COOEt \...
Consider the above reaction in which compound (A) on reaction with EAA(MeCOCH2COOEt) in the presence of NaOEt/EtOH gives a product which on hydrolysis and decarboxylation can give three compounds by different mechanisms.
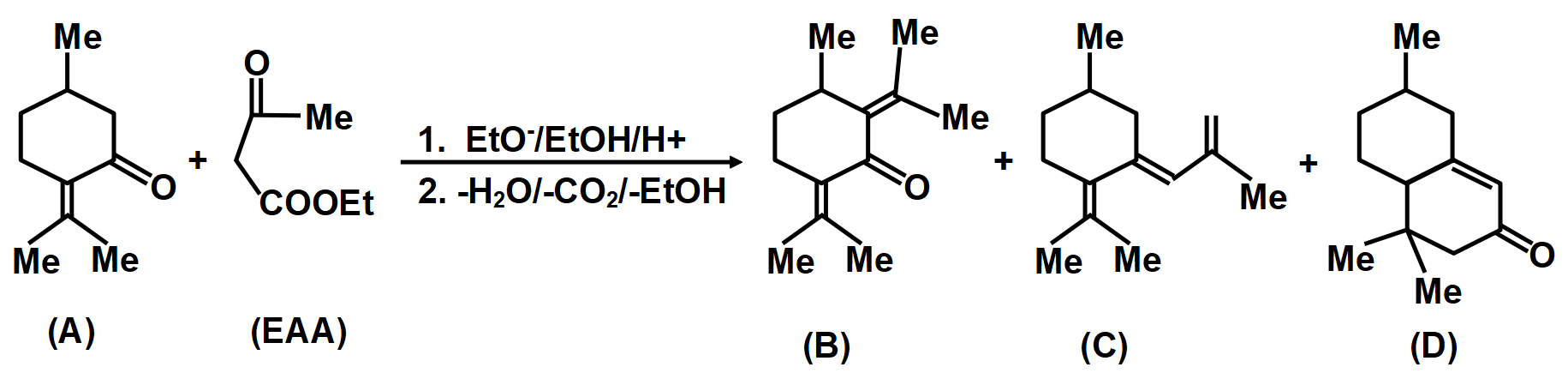
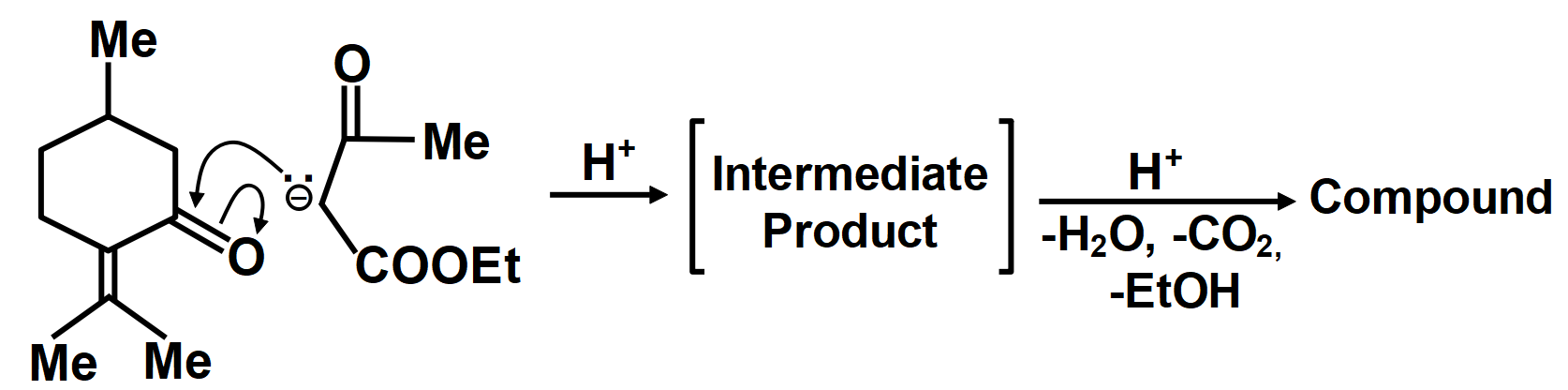
In another mechanism, EAA is carbanion source and (C=O) group of (A) is the acceptor. Give the compounds formed by the aldol product resulting from this mechanism, followed by hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
A.Compound (B)
B.Compound (C)
C.Compound (D)
D.None of the Above
Solution
We know that the carboxylic addition to the enol group reacts in a protonated form where the addition product is obtained which on dehydration yields the condensation product. Decarboxylation is the chemical reaction which removes a carboxyl group with the release of carbon dioxide gas.
Complete answer:
As we know that the oxidation of alkylbenzenes can be used to make aromatic carboxylic acids. Aromatic carboxylic acid compounds can be formed by vigorous oxidation of alkylbenzene compounds with acidic or alkaline potassium permanganate or chromic acid. The reaction's side products differ depending on whether the primary or secondary alkyl groups are present. The tertiary alkyl group, on the other hand, is unaffected. Furthermore, with the aid of these oxidizing agents, properly substituted alkenes can be oxidized to form carboxylic acids. The chemical reaction where a carboxyl group (−COOH) gets eliminated and carbon dioxide (CO2) is released at the product end is called Decarboxylation. The liberation of CO2 makes the reaction almost irreversible in many cases. However, the reverse process i.e. Carboxylation is the addition of CO2.The compound formed from the above-described mechanism is compound (C).
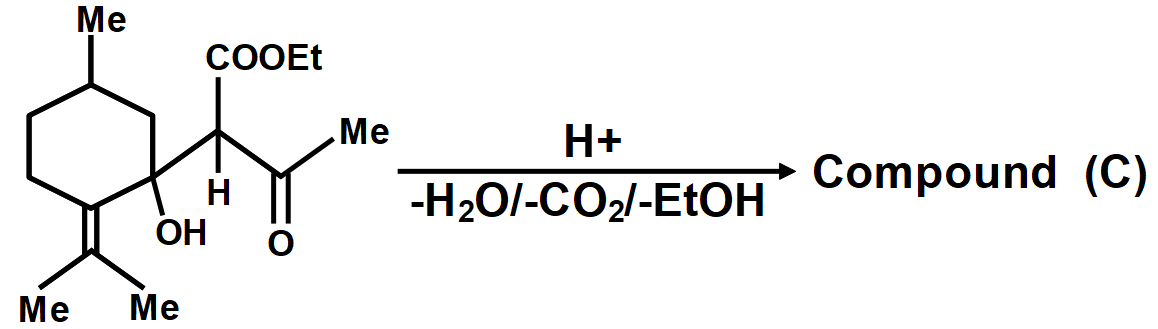
Carboxylic acids are the organic decarboxylation acids written as RCOOH, where R stands for an alkyl group or Hydrogen. The decarboxylation of a carboxylic acid is one of the oldest reactions discovered in organic chemistry. The reaction process involves the removal of -COOH group or a carboxylate salt of the given acid. The reaction gives the product RH along with CO2. Thus the complete reaction is given by;
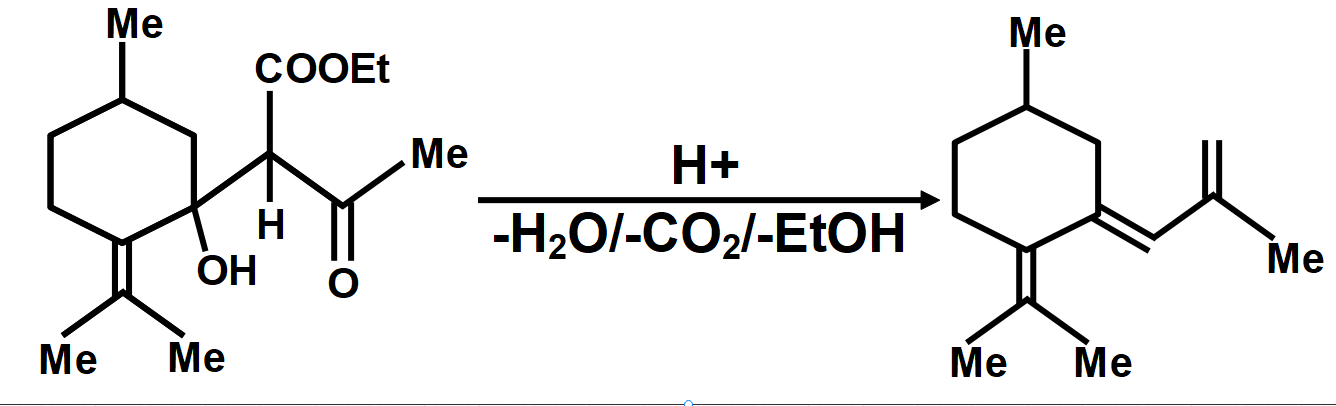
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
Remember that the carboxylic acids are formed when acid chlorides are hydrolyzed with water. Furthermore, acid chlorides can be quickly hydrolyzed with an aqueous base to create carboxylate ions, which can then be acidified to produce the desired carboxylic acids. Anhydrides, on the other hand, is hydrolyzed with water to create the appropriate acid.
