Question
Question: Consider an electric circuit with a diode. What will be the average power dissipated in the resistor...
Consider an electric circuit with a diode. What will be the average power dissipated in the resistor? (Assume diode is ideal)
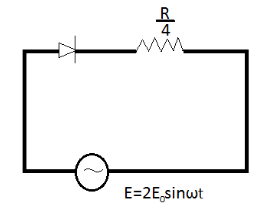
\left( A \right)\dfrac{{32{E_0}^2}}{R} \\\
\left( B \right)\dfrac{{16{E_0}^2}}{R} \\\
\left( C \right)\dfrac{{4{E_0}^2}}{R} \\\
\left( D \right)\dfrac{{{E_0}^2}}{{2R}} \\\
Solution
Hint : In order to solve this question, we are going to first consider the two cases for the circuit, one with a diode and the other without a diode, after that, we need to calculate the power of the case without the diode, and then, from the formula , we calculate the power for the circuit with a diode.
The power dissipated by the diode can be calculated as:
PD=21P0
Where PD is the power dissipated with a diode while P0 is the power dissipated without a diode
Power of circuit without diode
P0=21×resistancevoltage2 .
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us start by taking two cases of the circuit, first with a diode which is given in the above circuit and second without a diode.
With a diode:
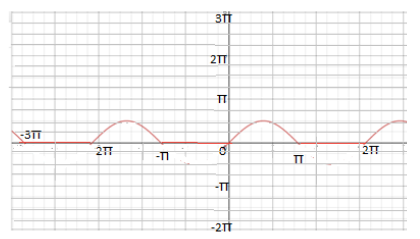
Without a diode:
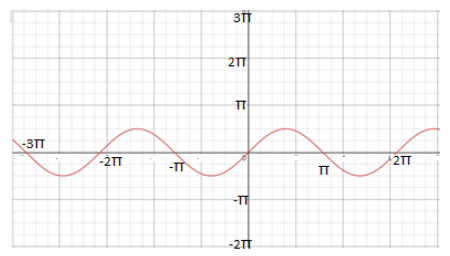
The power dissipated by the diode can be calculated as:
PD=21P0
Where PD is the power dissipated with a diode while P0 is the power dissipated without a diode
Now, without the diode, the power is given by:
P0=21×4R(22E0)2
Putting this in the above equation to calculate the power without a diode, we get
PD=21×4R(22E0)2=R4E02
Hence, option (C)R4E02 is the correct answer.
Note :
The key function of an ideal diode is to control the direction of current-flow. Current passing through a diode can only go in one direction, called the forward direction. Current trying to flow the reverse direction is blocked. By applying a diode in the circuit, the power becomes half of that of the power without diode.
