Question
Question: : Compound X on catalytic hydrogenation gives 2,6-dimethyloctane, on ozonolysis followed by the trea...
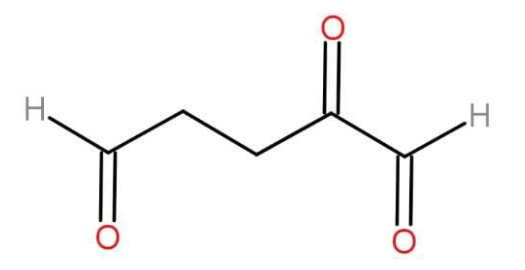
: Compound X on catalytic hydrogenation gives 2,6-dimethyloctane, on ozonolysis followed by the treatment with Zn−H2O , X yields formaldehyde, acetone and di aldehyde shown below. The most likely structure of the starting compound X is:
A.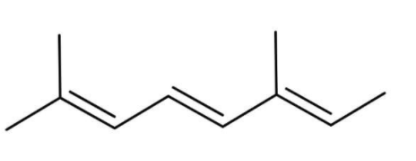
B.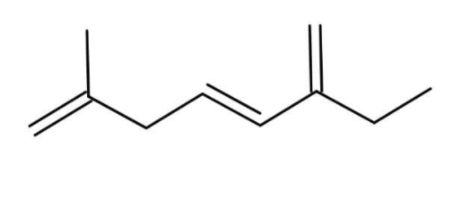
C.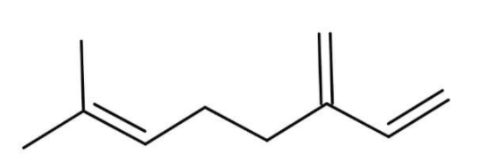
D.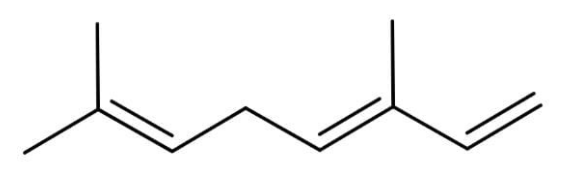
Solution
The corresponding alkene that will show the above reactions will contain 8 carbon atoms and 3 pi bonds out of which one pi bond will be in conjugation and will be at cis position to each other.
Complete answer:
Catalytic hydrogenation is the hydrogenation in the presence of some catalyst. Hydrogenation refers to the process of addition of hydrogen in a molecule. The catalyst used while hydrogenation is metal such as Raney nickel, platinum and palladium. The hydrogen gets adsorbed on the surfaces of these metals. The addition of 1 molecule of hydrogen occurs in one alkene. The hydrogenation of the following molecule will give us the 2,6-dimethyloctane. The hydrogen will add to each carbon making the double bond. The reaction will occur as:
Ozonolysis is the process of addition of oxygen molecule within a molecule containing double bond. A 3 member ring containing oxygen is formed first and then when we react it with a reducing agent such as zinc and water then the cyclic rings break down and form an aldehyde, a ketone and di aldehyde.
When we will do hydrogenation all the double bonds will get converted to the single bonds. And we will get one methyl group at the second position and one methyl group at the sixth position. So this will make the alkane formed as 2,6-dimethyloctane.
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note:
The energy releases when one mole of alkene is converted to alkane by addition of hydrogen is known as heat of hydrogenation. The alkane formed is more stable because at the cost of one weak pi bond 2 strong sigma bonds are formed.
