Question
Question: Compound ‘X’ having molecular formula\[\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text...
Compound ‘X’ having molecular formula C4H8O3 . It evolves CO2 , with NaHCO3 ’ X’ on reaction with LiAlH4 gives achiral compound ‘X’ is /are:
| A) | 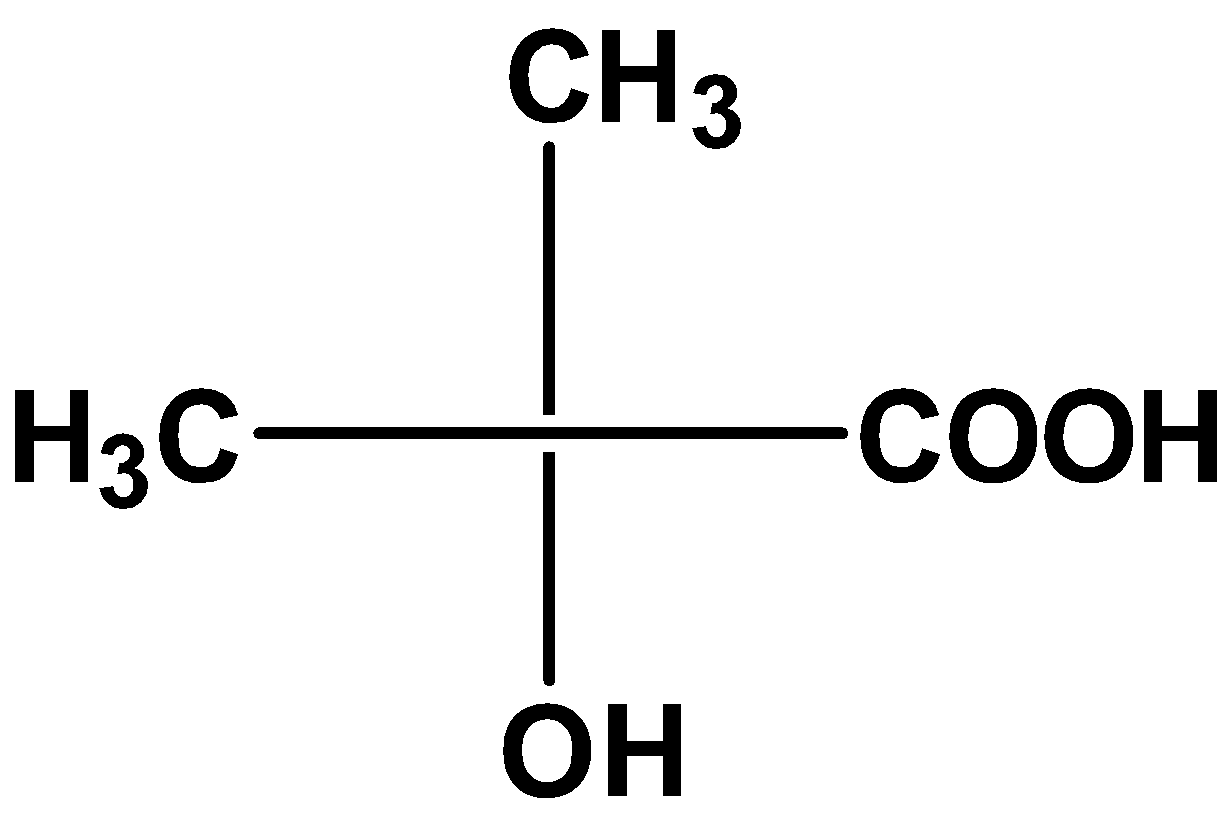 |
|---|---|
| B) | 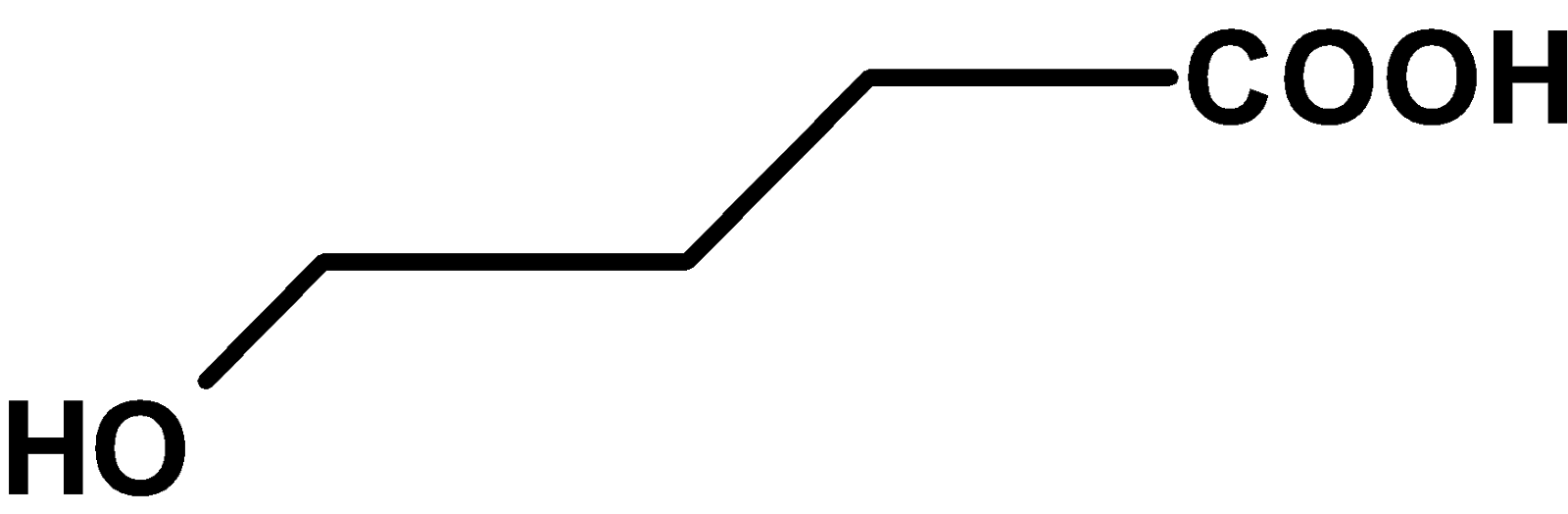 |
| C) | 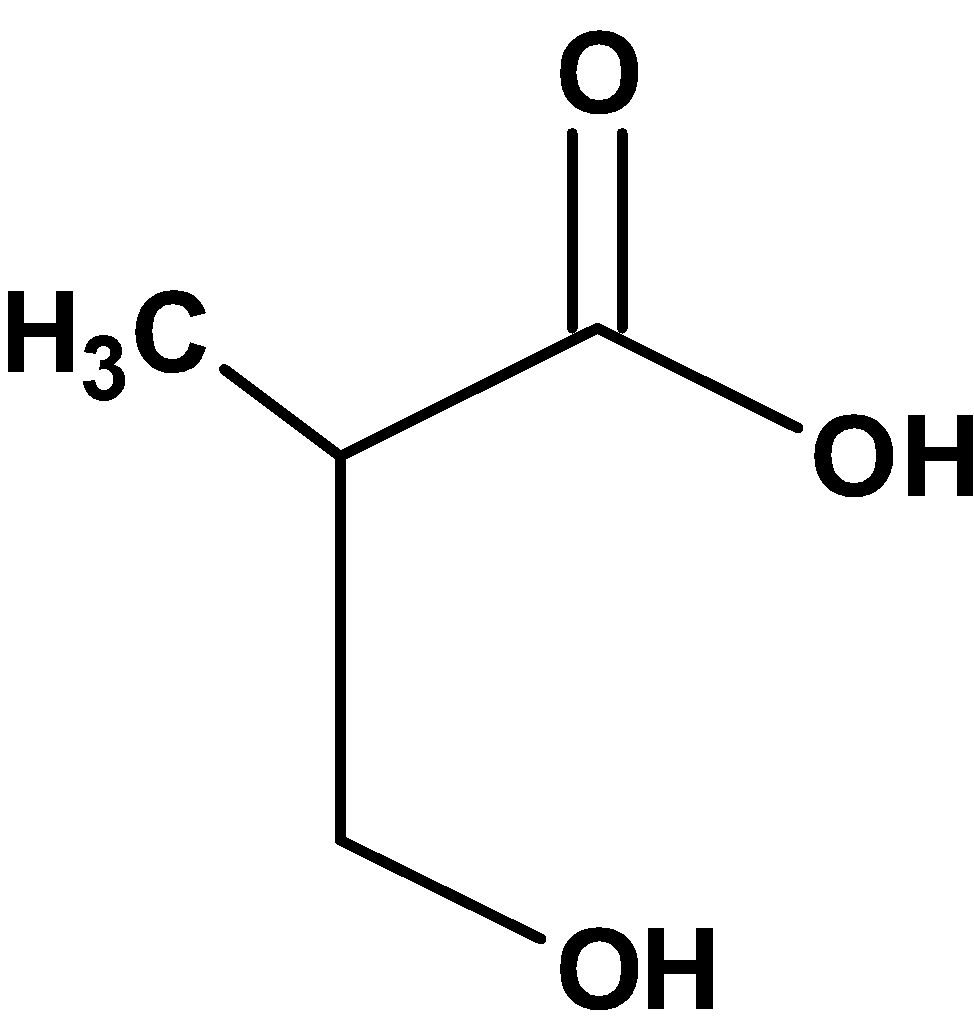 |
| D) | 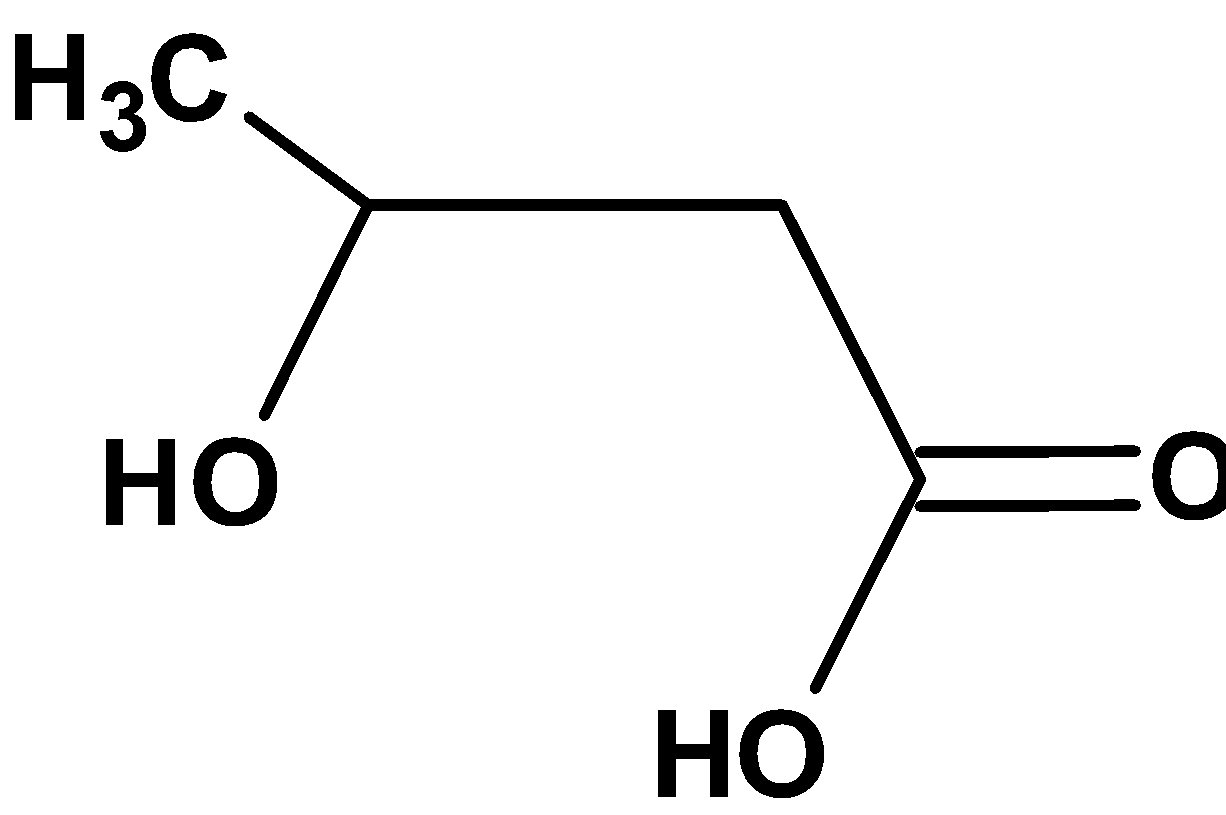 |
Solution
Carboxylic acid reacts with the carbonate or the bicarbonate. The reaction results in the evolution of carbon dioxide. The reducing agent like lithium aluminium hydride (LAH) adds the hydrogen atom across the compound. The carbonyl group in the compound is reduced to the hydroxyl group. Here, the compound on reduction with LAH forms an achiral compound.
Complete answer:
We have given that the compound ‘X’ which have the molecular formula C4H8O3 . When it is reacted with NaHCO3 evolves CO2 . The general reaction can be written as,
X NaHCO3 CO2
The compound ‘X’ also reacts with lithium aluminium hydride LiAlH4 .
Carboxylic acid reacts with the carbonates or the bicarbonates .The reaction of the carboxylic acid with aqueous sodium bicarbonate leads to the evolution of carbon dioxide producing brisk effervesces.
It may be noted that the carboxylic acid with the Na2CO3 or NaHCO3 , the carbon dioxide comes from the Na2CO3 or NaHCO3 and not from the carboxyl groups. The general reaction of the carboxylic acid with the sodium bicarbonate is given as follows,
RCOOH + NaHCO3 → RCOONa + CO2 + H2O
The compound C4H8O3 contains three oxygen atoms. Thus, the compound includes carboxylic acid groups and aldehydic groups or carboxylic acid groups and hydroxyl groups.
However, the 4 carbon atom compound with the aldehydic group and carboxylic acid group has the molecular formula equal to C4H8O3 .
The reaction between the NaHCO3 and compound X is given as,
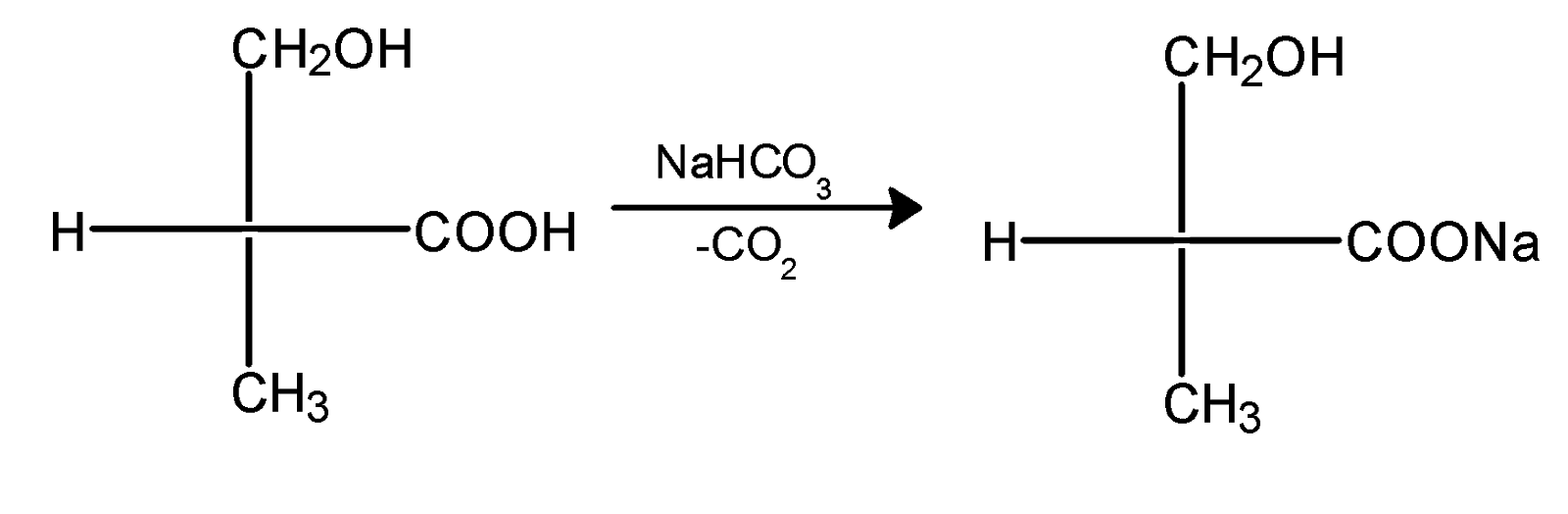
Lithium aluminium hydride is a reducing agent. It provides the hydrogen atom to the organic molecule. The acids can be reduced by lithium aluminium hydride. The carboxylic acid can be converted into the primary alcohol .T
The reaction of compound X with the LAH is as follows,
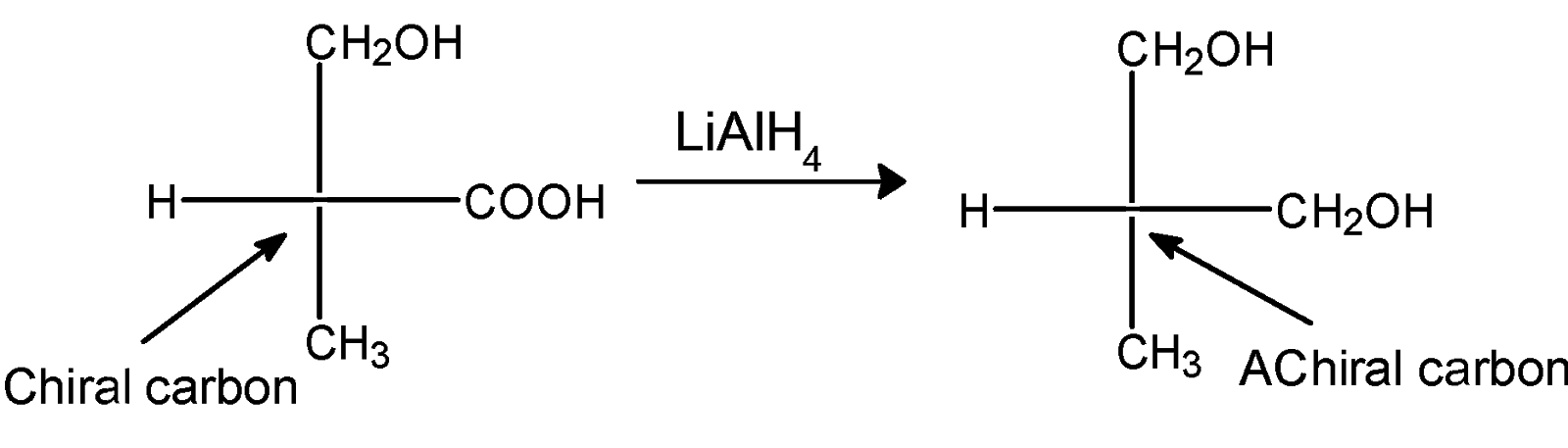
Thus, compound X from the option is,
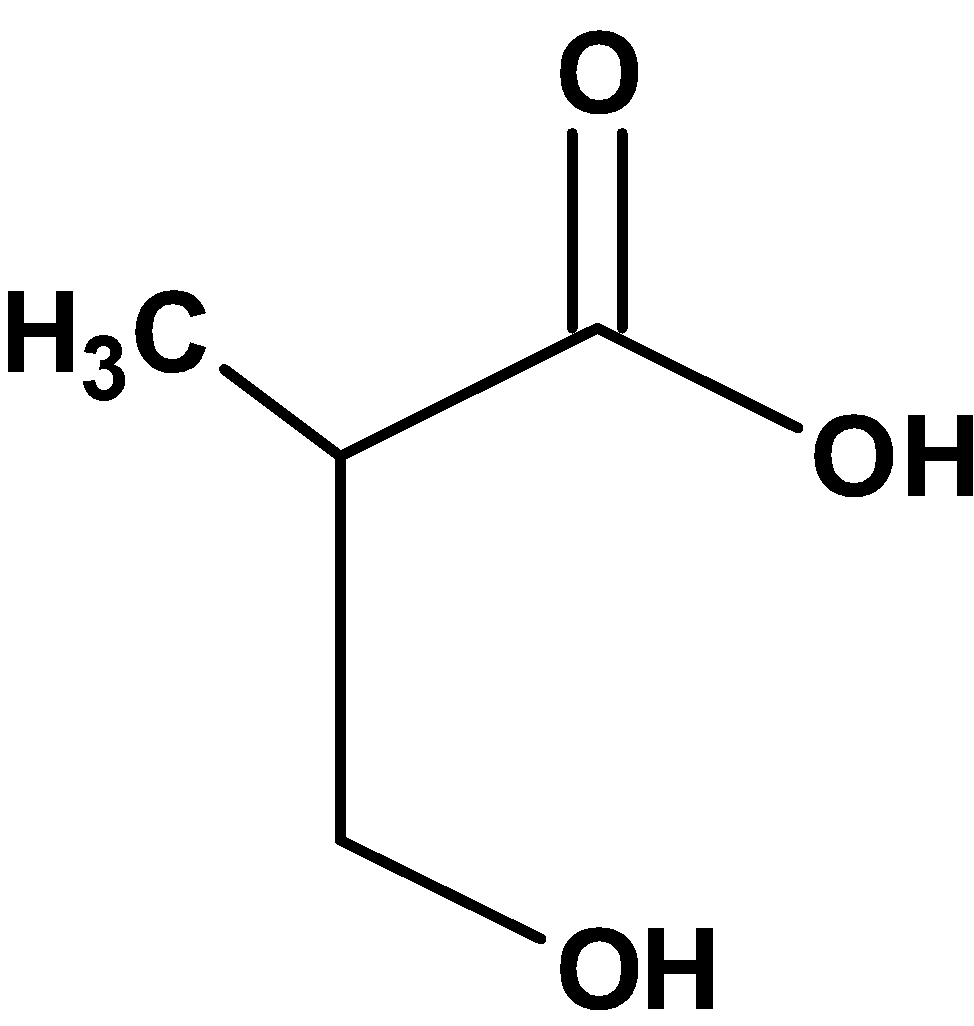
Hence, (C) is the correct option.
Note:
Note that, the reduction of acid or ester to the alcohol is easily carried out in presence of lithium aluminium hydride, but the reduction is not easily carried out by the sodium borohydride NaBH4 . This is because NaBH4 is a mild and selective reducing agent. The phenols do not produces effervescence when reacted with the bicarbonate, thus reaction with bicarbonate is used to distinguish between the phenol and carboxylic acid
