Question
Question: Compound ‘R’ on heating with \[{\text{aq}}{\text{.NaOH}}\] evolves \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}...
Compound ‘R’ on heating with aq.NaOH evolves NH3 gas.On heating with bromine inaq.NaOH evolves CO2 gas.With NaNO2/HCl,it evolves N2 gas.Compound ‘R’ is;
A.
B. 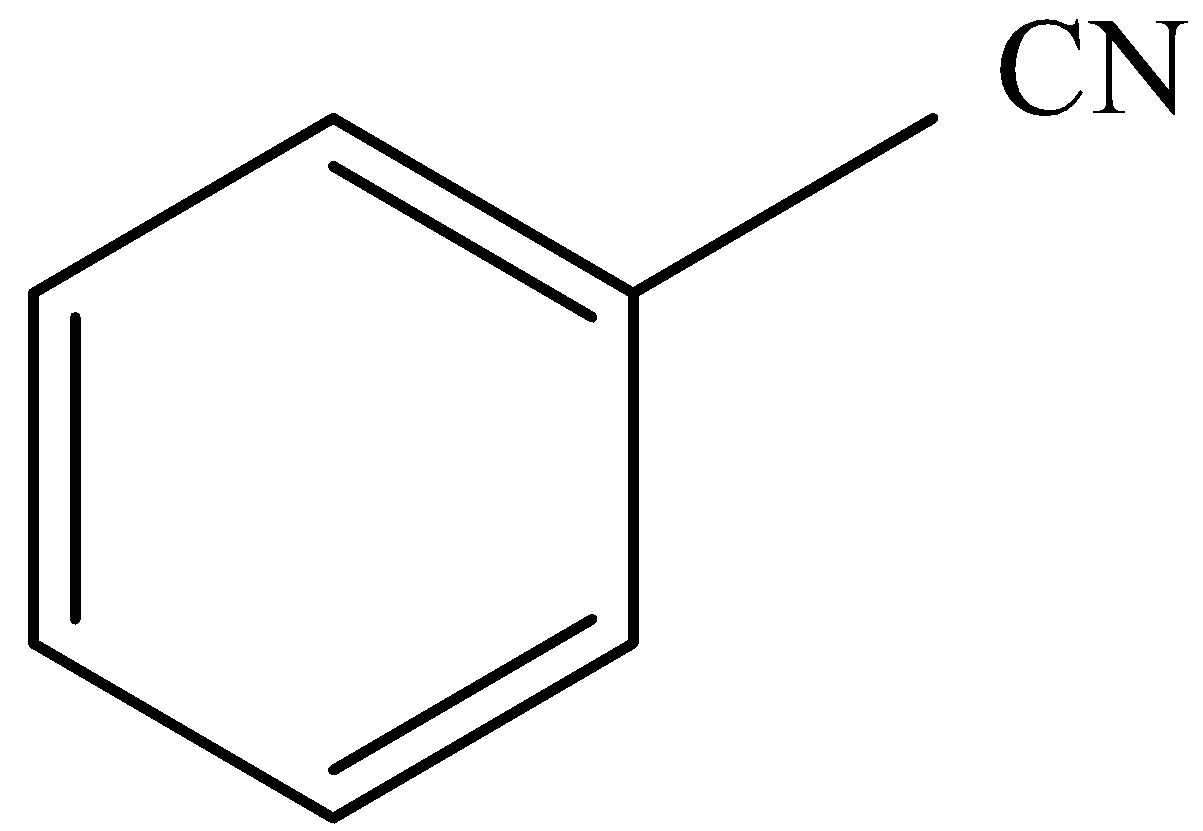
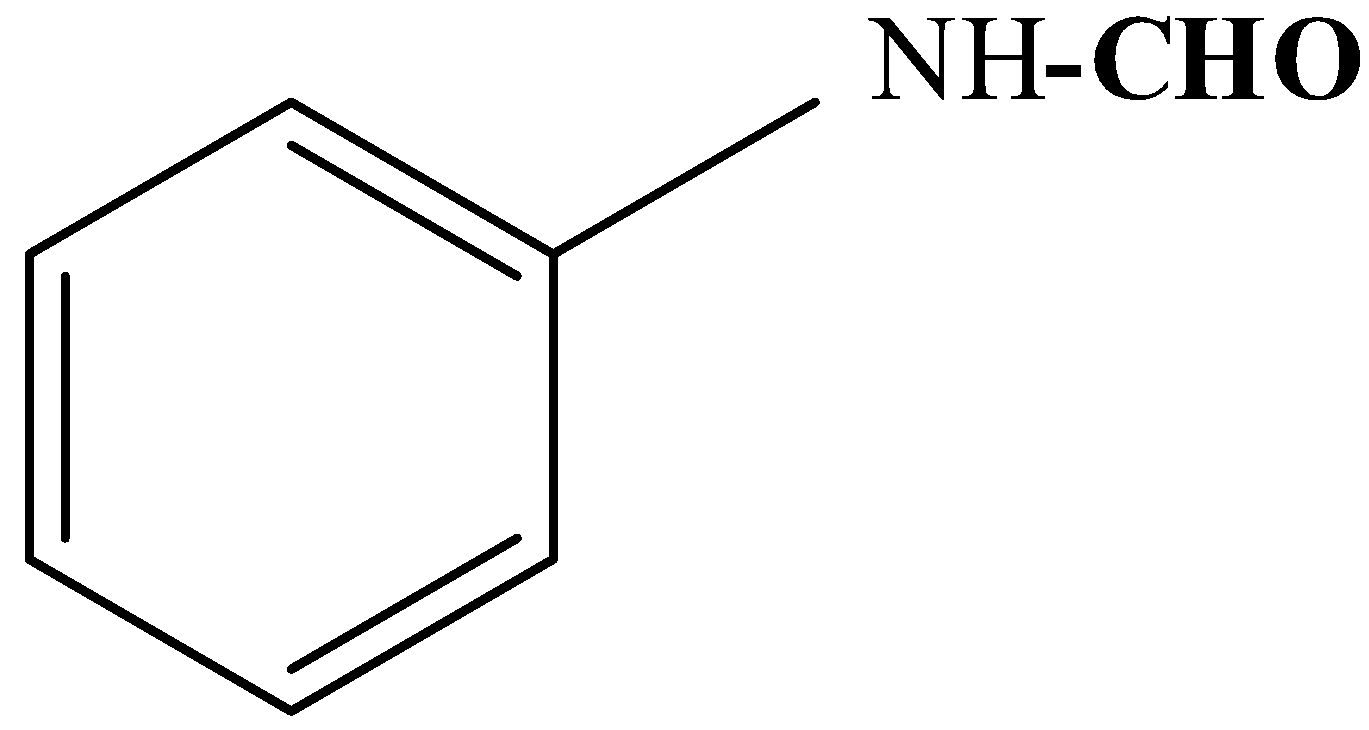
. 
C.
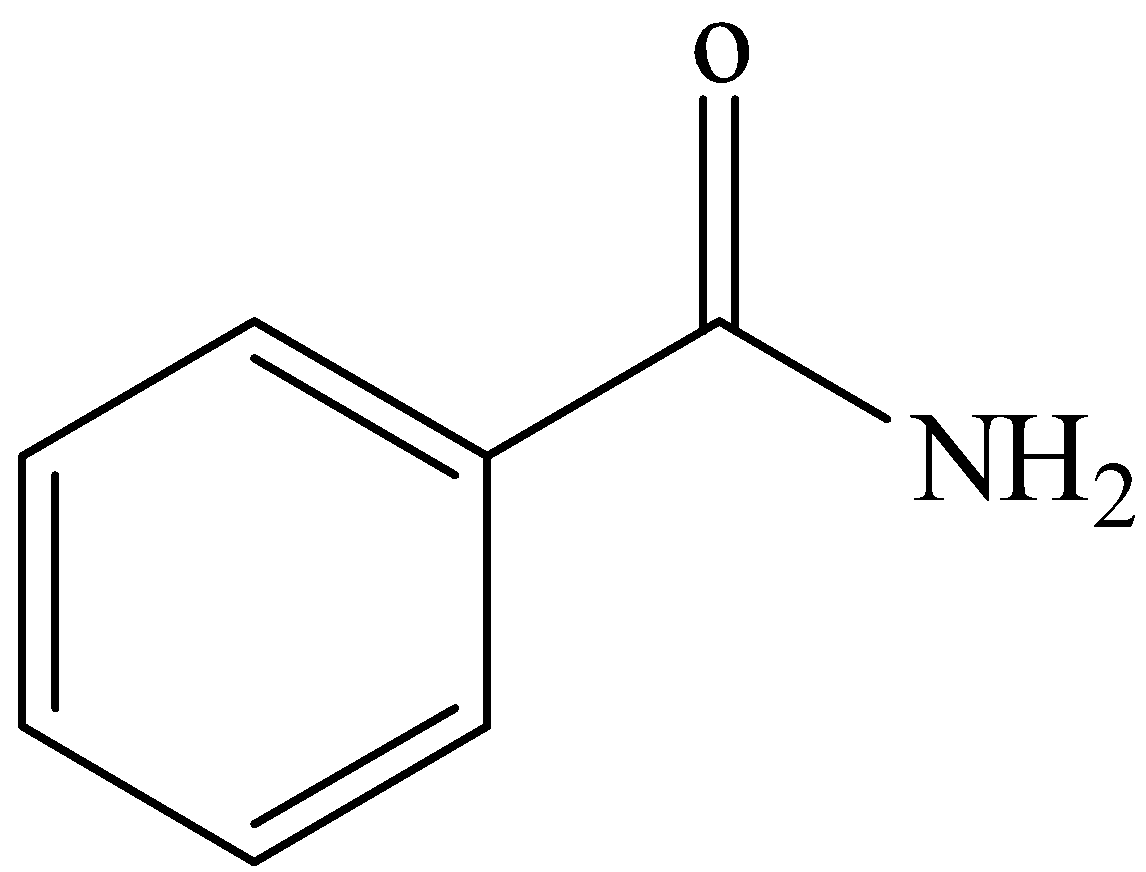
D.
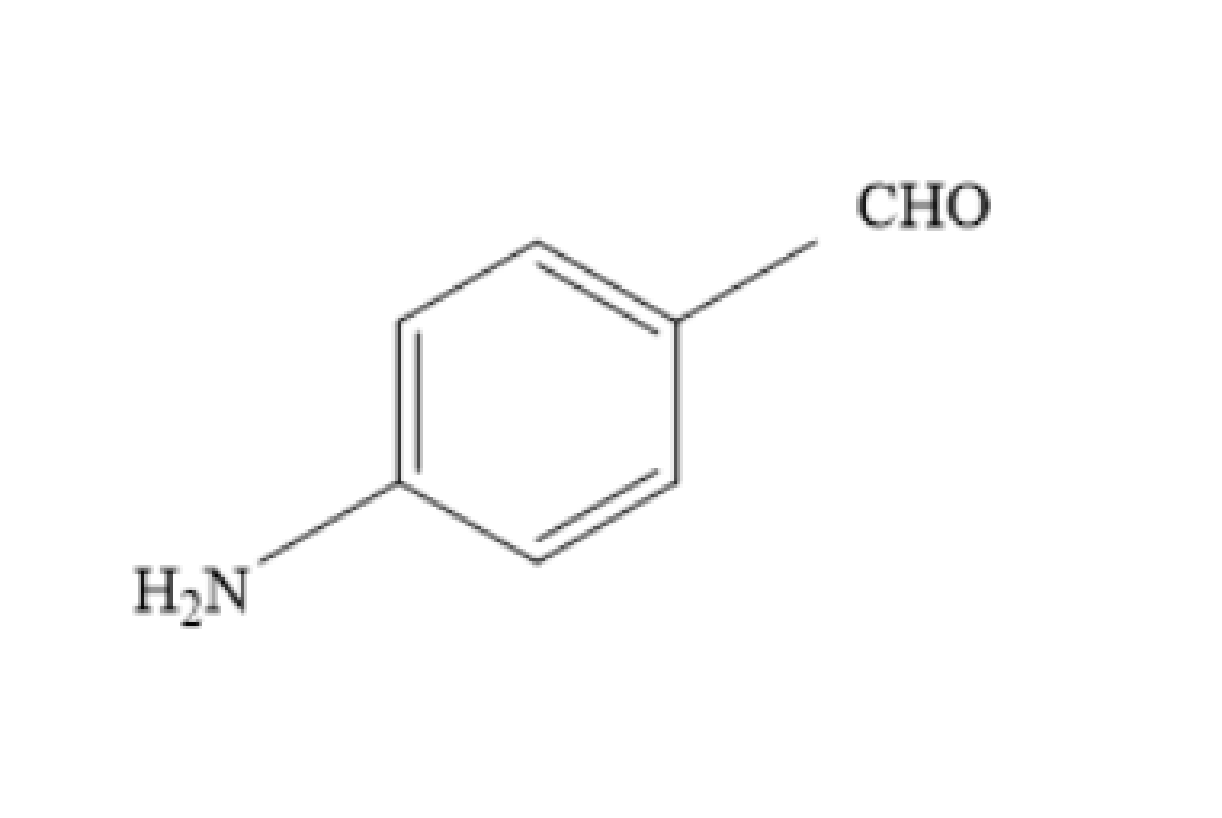
Solution
The above stated compound R will be an aromatic compound. It undergoes mainly three reactions. At first it is hydrolysed when heated with aq.NaOH . Then it undergoes Hoffmann Bromamide reaction. Finally, it is diazotized when treated with NaNO2/HCl. The compound that undergoes these reactions will be surely an aromatic compound.
Complete step by step answer:
The compound when heated with aq.NaOH gives the NH3 gas which means that there is the presence of an -NH2 group.
The reaction with heating the compound with Bromine in aq.NaOH is the Hoffmann Bromamide reaction. In this reaction the amides are converted to primary amines with one carbon atom less than the parent amide. Here RCONH2 gets converted to RNH2.
And finally, when this RNH2 is treated with NaNO2/HCl, the diazonium salt of the corresponding compound is formed.
From these reactions we can make sure that the compound contains a- CONH2 group and it is an aromatic compound. Therefore, the compound R will be benzamide. The three reactions can be shown as below:
1.Heating with aq.NaOH
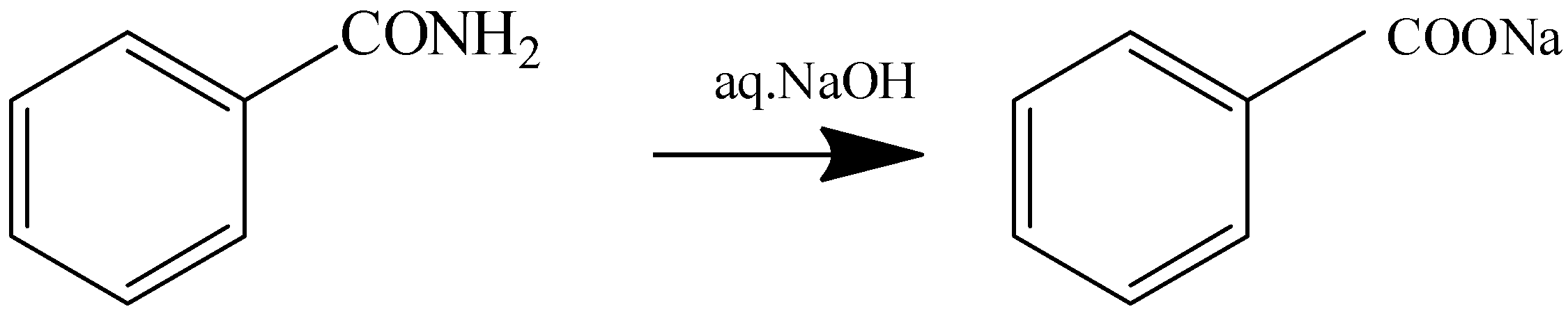
Benzamide Sodium Benzoate
2.Hoffmann Bromamide Reaction
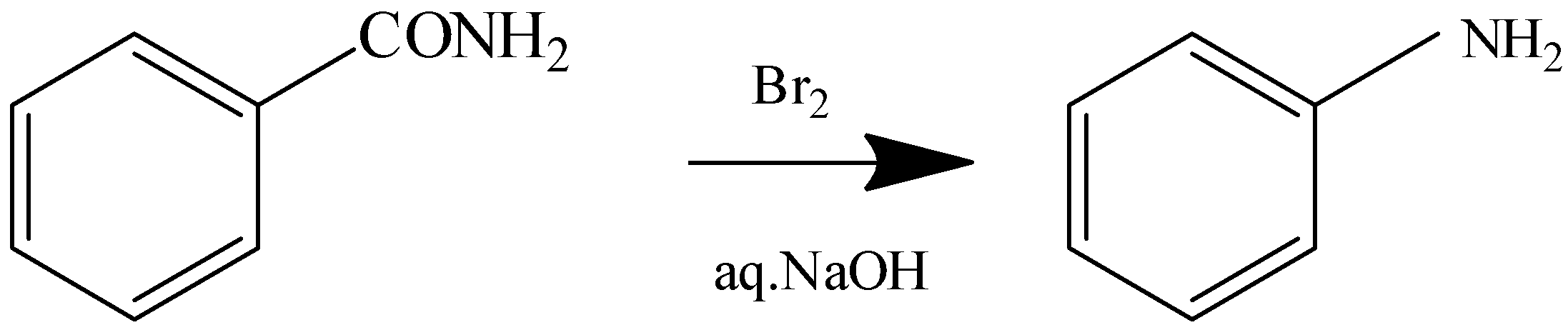
Benzamide Aniline
3.Diazotisation
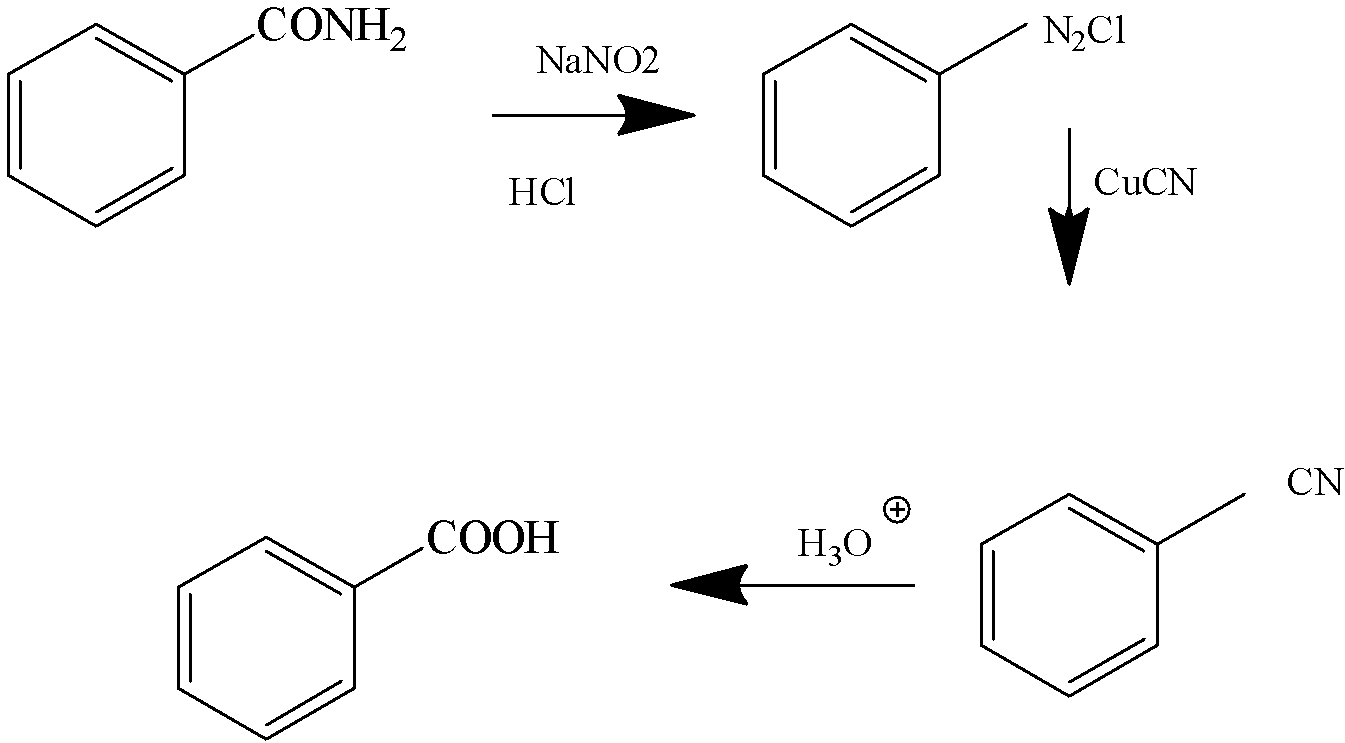
Benzoic Acid Benzonitrile
From these reactions we are clear that the compound R is Benzamide, C6H5CONH2.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Additional Information:
Amides are a group of chemicals with general formula RCONH2. Amides are divided into subclasses according to the number of substituents on the nitrogen atom. Benzamide is an aromatic amide having a benzene ring attached to the amide group.
Note: Hoffmann Bromamide reaction is an important organic named reaction. It is used to convert amides into primary amines with one carbon atom less than the parent amide. Also, the diazotization reaction is also an important intermediate reaction in the preparation of a wide variety of organic compounds.
